Index A-Z - Street

Aehra Afeela Aito AI-WAYS Arcfox Aptera ARI Motors Arrival Avatr BeyonCa BYD Byton CANOO Ceer Cenntro Delorean Deepal Evergrande New Energy Auto Evum Motors Faraday Future Fisker GAC Aion Galaxy Hozon Auto (Neta) Human Horizons Hycan IM Motors Ineos Automotive Izera Leapmotor Li Auto Lightyear Liux Lordstown Motors Lucid Motors Mullen Technologies Munro Vehicles Neta Auto NIO Olymp Cars Ora Polestar REE Automotive Rimac Automobili Rising Auto Rivian Automotive Seres Slate Auto Sono Motors Tesla Togg Auto Vinfast Voyah Xiaomi Xpeng Zeekr
Aehra is a BEV start-up startup from Italy that claims to combine Italian design, world-class engineering, and American customer service [1].
AEHRA plans to launch two models: a large SUV coupe and a four-door sedan. Both vehicles will be based on a newly developed, all-electric platform and equipped with a 120 kWh battery. The target range is around 800 kilometers, with a top speed of around 265 km/h.
The interior features a very wide, fully digital front display across the entire width of the vehicle and a second control panel in the center console. The cockpit uses a yoke-like steering wheel and follows a minimalist, futuristic operating concept. Despite its sporty proportions, the interior is expected to be spacious.

Aehra SUV
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of AEHRA Inc. [Homepage])

Aehra Limousine
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of AEHRA Inc. [Press Kit])
In terms of price, AEHRA is clearly positioned in the upper premium segment; the expected price per vehicle is around €160,000 to €180,000. Production is scheduled to start in 2026 at the earliest, with a possible ramp-up in production from 2027.
There are indications of financial and structural challenges in the company’s development. Several media outlets report that the start-up has so far lacked important investors and technical partners, which has already led to delays in the originally announced schedule. AEHRA has also applied for substantial government subsidies to enable it to build up its own production capacities. This dependence on external sources of financing and the postponement of the start of production indicate that the business model is currently under increased financial pressure.
Sources
[1] https://www.aehra.com/ (Homepage, Access 27.09.2022, 13.09.2023)
[cs 27.09.2022, 13.09.2023, 01.12.2025]
Afeela is a new brand of the BEV joint-venture of Sony and Honda, which was founded in 2022 under the name Sony Honda Mobility Inc. The aim is to combine the respective competencies in the field of electronics and automotive engineering [1].
Sony wants to tap into the fast-growing market for automotive IT systems like Huawei and Alibaba, and is entering the automotive market via a joint venture. Honda gets a partner for the electrification of its product range, where there is definitely a need to catch up.
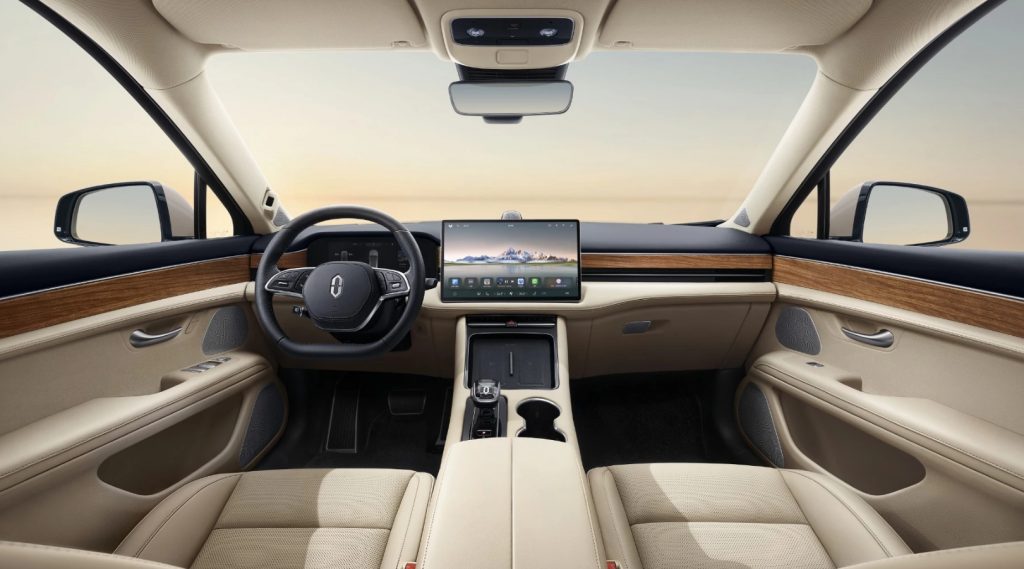
The first production model is a large, five-door sedan, with production scheduled to begin in the US in 2026. The vehicle uses two electric motors with all-wheel drive and a battery with around 91 kWh. The interior is largely based on Sony’s digital and entertainment focus. The cockpit consists of a wide display front with software-centered operating logic.
Afeela relies on an extensive sensor structure consisting of around 40 units, including cameras, radar, and LiDAR, to enable advanced assistance functions and semi-autonomous driving. This is complemented by comfort features such as air suspension and a modern interior design.
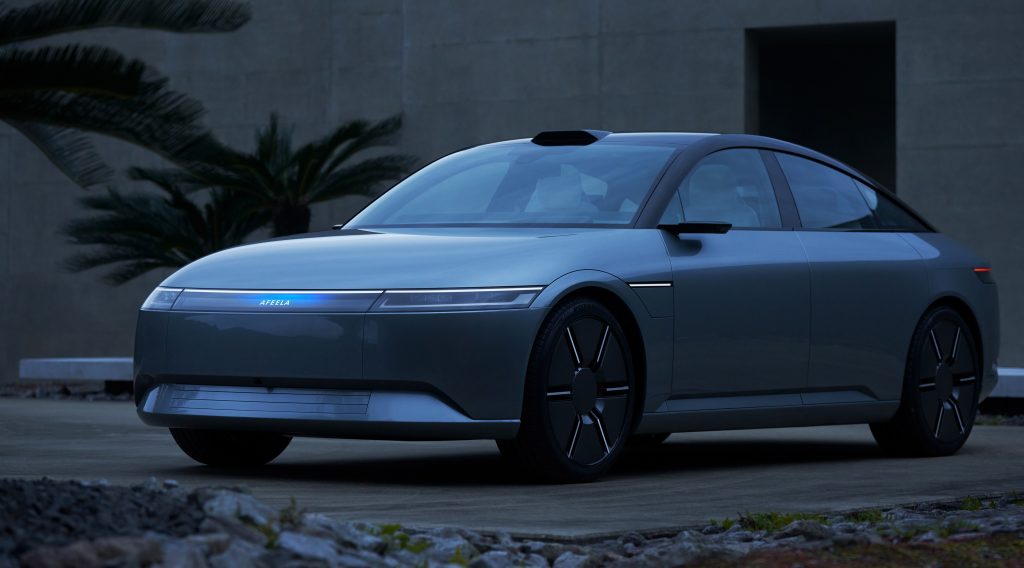

Afeela – Exterieur
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of Sony Honda Mobility Inc. [Gallery])

Afeela – Interieur
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of Sony Honda Mobility Inc. [Homepage])
Afeela is positioned in the premium segment, with entry-level models starting at around $90,000 and higher-spec versions costing around $100,000. The market launch will initially focus on North America.
For the fiscal year ending March 2025, Sony Honda Mobility reported an operating loss of around ¥52 billion (≈ $360 million). The introduction of a new premium EV requires high investments in software, sensor technology, and production setup and takes place in a highly competitive market segment. Despite these risks, however, the project is considered financially secure, as both owners—Sony and Honda—are very capital-strong corporations and offer the necessary stability for the start-up phase of the joint venture.
There is still no information about the powertrain components, such as the electric motor or the HV battery.
Sources
[1] https://www.shm-afeela.com/en/ (Homepage, Access 07.02.2023)
[cs 07.02.2023, 02.12.2025]
Aito is a Chinese electric vehicle brand developed and produced by the Seres Group, with Huawei involved in the design, software, and sales as a technology and distribution partner [1]. Huawei itself does not own the brand, but supplies key systems such as its HarmonyOS operating system and technologies for the assistance systems. In addition, Huawei sells Aito brand vehicles through its own showrooms.
Due to the close cooperation between Seres and Huawei, Aito is considered a BEV joint venture, even though it is not a joint venture in the legal sense. The aim of the collaboration is to create synergies between an electronics group and an automobile manufacturer:
- Huawei wants to tap into new markets and place its products in cars.
- Seres benefits from the IT expertise of its electronics partner.
AITO is positioning itself in the luxury segment, focusing primarily on SUV models with electric or range extender drives.
After its market launch, AITO quickly became one of the fastest-growing brands in the Chinese premium EV segment. According to official figures, the brand achieved sales of around 94,000 vehicles in 2023. This was followed by a significant increase to a total of around 387,000 units in 2024, driven primarily by the success of the large AITO M9 SUV, which achieved sales of over 200,000 in its first year. Complete annual figures for 2025 are not yet available, but by August 2025, AITO had reported cumulative deliveries of around 770,000 vehicles since its market launch, meaning that high sales levels can once again be expected for 2025.

Aito M5 EV – Exterieur
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of Aito [Press Release])

Aito M5 EV – Interieur
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of Aito [Press Release])
AITO is now also working on international expansion. At IAA Mobility 2025, the brand unveiled its first global model range with a view to gaining a foothold outside China. Initial indications suggest that individual models are also intended for the European market, but a specific market launch in Europe has not yet been confirmed. The focus of sales remains clearly on China.
Publicly available financial figures on the brand’s sales or profits are currently not available. The Seres Group does not publish separate financial figures for AITO, so the economic assessment is mainly based on sales volume and market presence.
Overall, AITO is showing strong growth, driven by a broad SUV portfolio, technological support from Huawei, and aggressive market dynamics in China. How the brand can establish itself internationally remains to be seen in view of its further expansion.
AITO sources its battery cells from CATL. A long-term strategic agreement has been in place between the manufacturer Seres and CATL since 2022, according to which AITO models will be equipped with CATL batteries until at least 2027. CATL battery systems such as the Qilin generation will be used, among others. New battery technologies have also been announced for upcoming AITO models, including a sodium-based CATL battery with very high fast-charging capability.
Sources
[1] https://aito.auto/ (Homepage, Access 08.02.2023)
[cs 08.02.2023, 03.06.2023, 02.12.2025]
AI-WAYS is a BEV start-up from China founded founded in Shanghai in 2017, the company has a subsidiary in Munich. The brand primarily offers the U5 and U6 SUV models, which have been in production since 2019 and 2021, respectively, and were also launched in several European markets in 2020.
From 2023 onwards, Aiways came under pressure as the Chinese EV market was characterized by overcapacity and fierce price competition. In 2024, the company officially withdrew from the Chinese market and has since focused exclusively on export markets, particularly Europe. At the same time, a structural realignment was initiated: a merger with the US SPAC Hudson Acquisition created the new company EuroEV Holdings, through which Aiways will operate in the future. Based on this transaction, Aiways was valued at approximately $410 million. In addition, the company plans to start local vehicle production in Europe in 2025 to stabilize supply chains and strengthen market access.

AI-WAYS U5
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of Aiways Automobile Europe GmbH [Galerien])

AI-WAYS U6
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of Aiways Automobile Europe GmbH [Galerien])
Sales figures in Europe have remained comparatively low in recent years: around 550 vehicles were registered in 2020, around 1,000 in 2021, and around 1,200 in 2022. Despite the low sales levels, Aiways is sticking to its international sales strategy and sees long-term potential in the European market.
Financially, Aiways has raised a total of around 5.2 billion yuan since its founding. The economic situation has been tense recently, but the international realignment, planned production in Europe, and capital structure via EuroEV Holdings are expected to open up new prospects for the company.
Sources
[1] https://www.ai-ways.eu/de/ (Homepage, Access 05.09.2022)
[cs 05.09.2022, 04.06.2023, 02.12.2025]
Arcfox was established as a new BEV brand brand within the BAIC Group. The BAIC Group was founded in Beijing in 1958 and is one of China’s state-owned automotive groups. In terms of vehicle sales, BAIC is one of the ten largest Chinese OEM groups; in 2025, the group sold around 1.75 million vehicles worldwide.
The brand is primarily aimed at the higher-end segment of the Chinese market and is intended to be the technological spearhead of electrification within the BAIC Group.
The first production model was the Arcfox αT electric SUV, which was launched in 2020. It was followed shortly thereafter by the Arcfox αS sedan. The portfolio was later expanded to include variants with advanced driver assistance technology developed in cooperation with the technology company Huawei.
Arcfox initially developed at a moderate pace, but by 2025 it had already sold six-figure numbers of vehicles for the first time
- In 2023, around 30,000 vehicles were delivered.
- In 2024, sales rose to around 81,000 units.
- In 2025, sales doubled to around 163,000 vehicles.
Unlike independently listed brands, no separate financial figures are published for Arcfox. The brand’s economic performance is directly incorporated into the overall balance sheet of the BAIC Group or its electric car subsidiary BAIC BJEV, which is responsible for the development, production, and distribution of the vehicles. Arcfox is the higher-end BEV brand within the group’s electrification strategy.
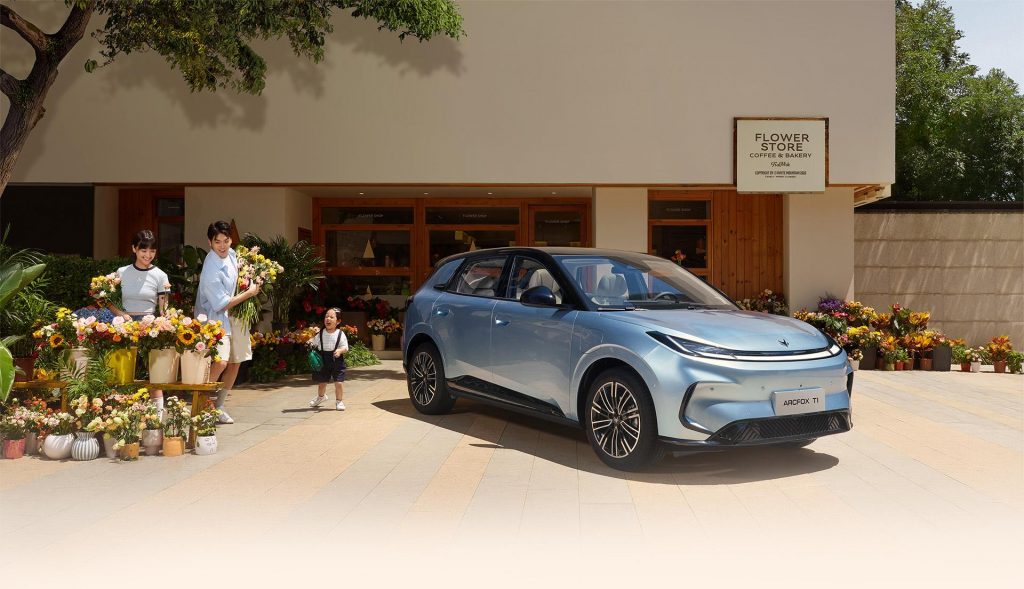

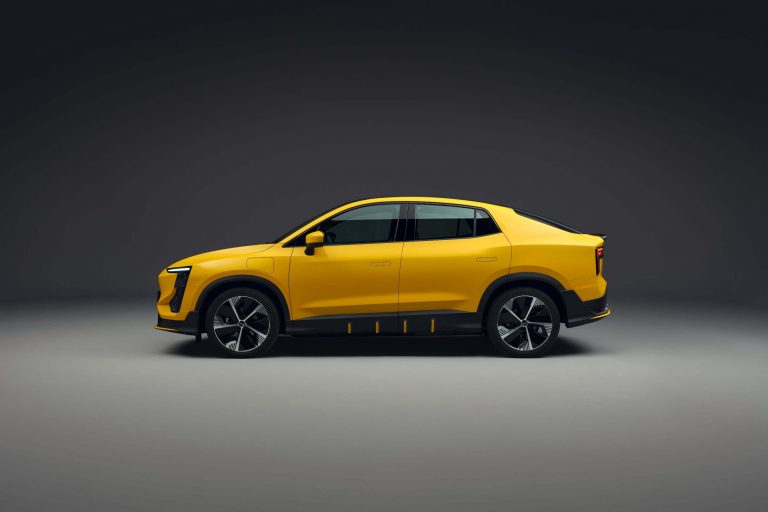
Arcfox T1 – Exterieur
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of ARCFOX. [Homepage])
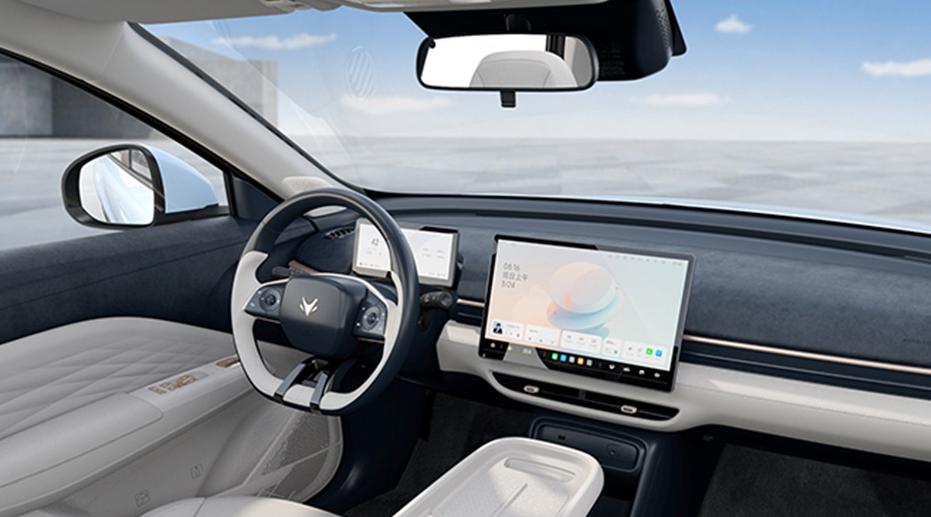

Arcfox T1 – Interieur
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of ARCFOX. [Homepage])
Arcfox models have so far been sold primarily in the Chinese domestic market, but are also being developed with an eye to international markets. Cooperation with the technology company Huawei also plays an important role. Certain variants—such as the αS with Huawei HI system—feature advanced driver assistance, software, and connectivity solutions. This cooperation underscores Arcfox’s strategic positioning as a technology-driven electric car brand within the BAIC Group.
When it comes to battery technology, Arcfox relies on cell manufacturers such as CATL and SK On CATL, using LFP and NMC cells.
The Arcfox brand belongs to the state-owned BAIC Group, which is majority-owned by the Beijing municipal government. The subsidiary BAIC Motor is listed on the Hong Kong stock exchange and bundles significant parts of the passenger car business. This gives the group access to the capital market, while the holding structure remains state-controlled.
Sources
[1] https://www.arcfox.com.cn/home_en.html (Access 10.03.2026)
[cs 10.03.2026]
Aptera is a Californian solar car start-up, that was only founded in 2019 by Chris Anthony and Steve Fambro in San Diego, although the founders had already been involved with electric vehicles before [1].
Aptera, along with Lightyear and Sono Motors, is one of the startups focusing on electric vehicles with solar cells, meaning that some of the electrical energy will be generated directly from the sun.
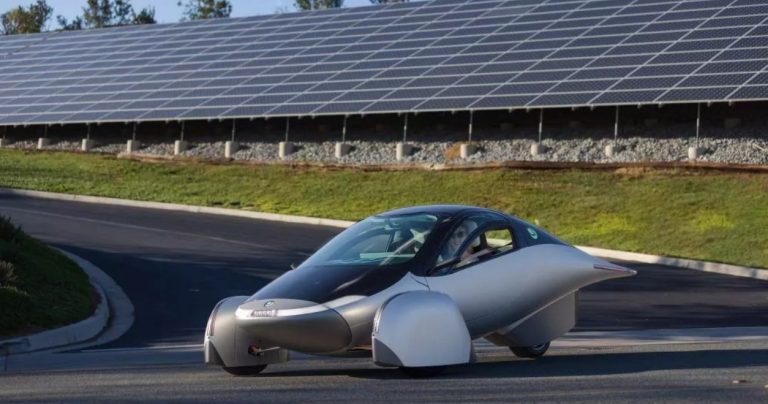

Aptera Model Gamma
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of Aptera Motors Corp. [Homepage])

Configurator Aptera Homepage
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of Aptera Motors Corp. [Homepage])
The entry price is $25,900 for the 250-mile (402 km) range version; optional ranges of 400, 600, or even 1000 miles (1609 km) can be configured; for the 1000-mile variant, the base price is $44,900 (see figure above).
The number of solar panels can also be configured, with an additional charge of €900 for the maximum configuration.
Up to 40 miles per day can be charged via the solar cells, which is roughly equivalent to the average daily driving distance in the USA. Especially for sun-drenched and densely populated Southern California, this idea of “driving without recharging” sounds fascinating, of course.
Aptera’s cell supplier is EVE Energy, using 21700 cells (21 mm diameter, 70 mm length) with NMC-811 chemistry (nickel/manganese/cobalt ratio of 8 to 1 to 1) [2].
Overall, the Aptera is a very exciting product, but it remains to be seen whether it will appeal to American consumers.
Sources
[1] https://aptera.us/ (Homepage, Access 13.02.2023)
[2] https://aptera.us/aptera-announces-battery-cell-supplier-eve-energy-co-ltd/ (Homepage, Access 13.02.2023)
[cs 13.02.2022]

ARI 458
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of ARI Motors GmbH [Homepage])
The vehicle platforms comes from the Chinese manufacturer Jiauan EV [2].
The cell supplier of Ari Motors or Jiauan EV is not known to the editors.
Sources
[1] https://ari-motors.com/ (Homepage, Access 17.09.2022)
[2] https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/ARI_Motors (Access 17.09.2022)
[cs 17.09.2022]
English BEV start-up founded in London in 2014 by Denis Sverdlov, but which has since had to be wound up.
Arrival wanted to manufacture electric delivery vans, small trucks, and buses in so-called “microfactories.” Instead of large factories, Arrival wanted many small, robotized locations in order to build electric transporters efficiently and flexibly. However, the concept proved too complex, and production delays, technical problems, massive cost explosions, and the failure to achieve serious series production led to doubts early on.
By 2022, the company was already reporting significant losses; the debut van never went into series production. As a result, capital raising and investor confidence collapsed. In January 2024, trading on the stock exchange was suspended and shortly thereafter the delisting decision was implemented. On May 22, 2024, the group was officially declared bankrupt.
[cs 20.09.2022, 02.12.2025]
Avatr is a Chinese BEV joint-venture established by Changan and Nio in 2018. Changan is a state-owned car manufacturer, which was founded back in 1862 to produce military equipment, among the four major state-owned car companies in China, Changan ranks 4th.
Meanwhile, Nio has withdrawn from the company again, CATL has entered instead. Huawei is assisting with development but does not have a stake in the company. The first model is the AVATR 11, an attractive midsize SUV coupe equipped with CATL’s new cell-to-pack technology. According to the press release, other technical specifications include a 750-volt platform, a range of 680 km according to CLTC, 200 km of range in 10 minutes of charging, and classic NMC cell chemistry.
This was followed by the AVATR 12, 07, and 06. In 2024, Avatr achieved 73,606 deliveries, with further growth expected in 2025, with over 10,000 sales in March alone. Total sales in 2025 are estimated at 130,000 and 150,000 units.

Avatr 11 – Exterieur
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of Avatr Technology (Chongqing) Co., LTD. [Homepage])

Avatr 11 – Interieur
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of Avatr Technology (Chongqing) Co., LTD. [Homepage])
In its financial results, Avatr reported revenue of RMB 15.35 billion (≈ €1.84 billion) for 2024. Despite this growth, the company posted a net loss of around RMB 4.02 billion (≈ €480 million) in 2024 as it continued to invest heavily in development, brand building, and sales. In the first half of 2025, Avatr already achieved RMB 12.2 billion in revenue (≈ €1.46 billion), of which RMB 11.5 billion came from vehicle sales, but still recorded a small net loss of around RMB 15.9 million (≈ €2 million). The company emphasizes its goal of reaching the break-even point by the end of 2025.
A first step toward international visibility was its appearance at the IAA Mobility 2025 in Munich. There, Avatr presented several production models (including the AVATR 06, 07, and 11). However, the company has not yet provided specific dates for the market launch or first European deliveries.
Sources
[1] https://www.avatr.com/ (Homepage, Access 06.02.2023)
[cs 06.02.2022, 13.09.2023, 04.12.2025]
BeyonCa is a BEV-Start-up founded in 2022 by Renault China CEO Soh Weiming and Dongfeng Motor in China. Company locations include a headquarters in Beijing, a design center in Munich, and an artificial intelligence development site in Singapore.
The name stands for “Beyond Car”, which probably means “more than a car”; the “more” includes medical monitoring functions such as blood pressure measurements, which are to be integrated into the vehicle.

GT Opus 1 – Front
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of BeyonCa Information Technology Co., Ltd [Homepage])

GT Opus 1 – Back
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of BeyonCa Information Technology Co., Ltd [Homepage])
The first product is a premium sedan called GT Opus 1 with an operating voltage of 800 V and a HV battery with 130 kWh. In terms of gap dimensions, the company wants to follow the lead of German premium manufacturers, which it has also identified as its main competitors. The start of series production was originally planned for 2024, but this date could not be met [2].
There is currently no evidence of acute financial difficulties at BeyonCa, but there is still a lack of information on production, sales, and business figures. It is also striking that the last media entry on the official website dates back to 2024, which suggests reduced public communication. Given the strong consolidation pressure in the Chinese EV market, it cannot be ruled out that BeyonCa is also facing economic challenges, although there has been no official confirmation of this to date.
Sources
[1] http://www.beyonca.com/ (Homepage, Access 13.02.2023)
[2] https://www.auto-motor-und-sport.de/neuheiten/beyonca-gt-opus-1-super-premium-elektroauto/ (Access 13.02.2023)
[cs 06.02.2022, 05.12.2025]
BYD Company Limited (BYD for short) was founded as start-up for the production of battery cells in 1995 by Mr. Wang Chuanfu in the city of Shenzhen, with the abbreviation BYD standing for “Build Your Dream”. BYD also became an automobile manufacturer in 2003 by joining Xian Qinhuan Automobile. In March 2022, production of pure combustion engines was discontinued, meaning that BYD now focuses on pure electric vehicles (BEVs) and plug-in hybrids (PHEVs).
BYD’s current corporate structure comprises several key subsidiaries, including BYD Auto (vehicle production), BYD Electronics (electronics manufacturing), and BYD LED. The former joint venture Shenzhen BYD Daimler New Technology, originally founded together with Mercedes-Benz AG and known for the Denza brand, is now wholly owned by BYD after Mercedes-Benz withdrew from the joint venture.
BEV sales figures were still around 320,800 vehicles in 2021, but rose significantly in subsequent years:
- In 2022, more than 911,000 units were already delivered.
- In 2023, the million mark was exceeded for the first time with around 1,175,000 vehicles.
- In 2024, just under 1,765,000 units were delivered.
- In 2025, BYD overtook Tesla for the first time with nearly 2,260,000 vehicles sold, becoming the world’s largest BEV manufacturer.
In total, BYD sold more than 4.6 million new energy vehicles in the same year, propelling BYD into the league of the world’s largest vehicle manufacturers.
BYD has been one of the few profitable BEV start-ups for several years now:
- In 2023, the company achieved a revenue of RMB 602.3B (≈ € 79.1B) and a net profit of almost RMB 30.1B (≈ € 4B).
- In 2024, revenue increased to over RMB 777B (≈ € 99.3B) and profit reaching RMB 40.2B (≈ € 5.1B).
BYD gradually developed its hybrid technology; the so-called DM-i drive was introduced in the early 2020s and combines serial and parallel operation:
- In city traffic, the combustion engine usually functions as a power generator, while the electric motor takes over the drive.
- At higher speeds, the combustion engine can be mechanically engaged to improve efficiency and performance.
The DM-i hybrid system is now used in numerous models such as the Qin, Song, Tang, Seal U, and other series. The BYD Touring 6 with DM-i drive is now also to be exported to Europe. This drive technology could be particularly attractive in Germany, with its high highway speeds.

BYD Model Han – Exterieur
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of Hedin Electric Mobility GmbH [Homepage])

BYD Model Han – Interieur
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of Hedin Electric Mobility GmbH [Homepage])
In 2025, BYD exported over 1M vehicles abroad, accounting for around a quarter of its total sales:
- Around 600,000 units went to Europe, with countries such as Belgium, the United Kingdom, and Spain among the most important customers.
- An estimated 200,000–250,000 vehicles were delivered to Latin and Central America, with Brazil and Mexico receiving the lion’s share.
- Around 19,000 BYD vehicles were registered in Germany in 2025.
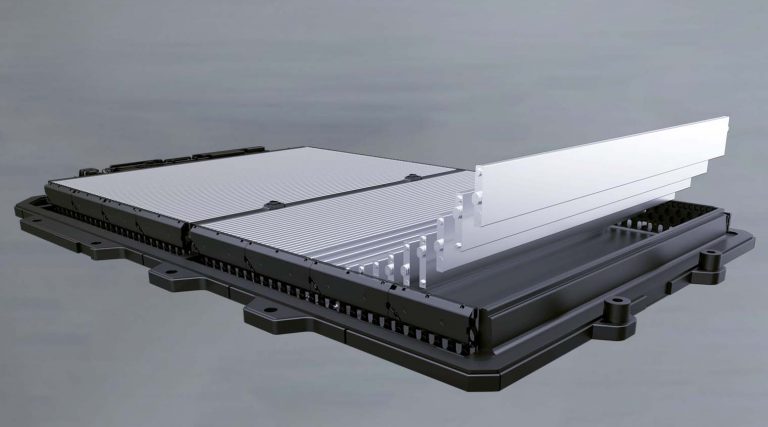

HV battery equipped with blade cells
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of BYD Company Ltd. [Homepage])
BYD’s battery activities are bundled in its subsidiary FinDreams Battery. There, battery cells, modules, and complete battery systems, including the associated cell chemistry, are developed independently and produced on a large scale. FinDreams supplies not only BYD’s own vehicle production, but also external OEMs, including Tesla and BorgWarner.
In 2025, FinDreams was the second-largest battery manufacturer worldwide with a market share of around 16.7%.
Blade cells are almost exclusively used in hybrid and electric vehicles. These are prismatic cells with an unusual length of up to almost one meter, which visually resemble a sword blade. The long blade cells are used in BEV models, while short cells are used in BYD’s hybrid vehicles.
The blade cell is only available with lithium iron phosphate (LFP) chemistry, which, unlike NMC chemistry, does not require critical raw materials such as nickel and cobalt and is significantly safer in terms of overheating and fire risk (thermal runaway). An HV battery built from Blade cells is designed to last 1.2 million kilometers or 3,000 charging cycles [2].
The disadvantage of iron phosphate cells compared to NMC cells is the lower energy density. When blade cells are used, this disadvantage is compensated by the very compact design that allows HV batteries to be composed of blade cells.
BYD is listed on the stock exchange, among others in Frankfurt under WKN A0M4W9 and ISIN CNE100000296.
Sources
[1] https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/BYD (Access 10.10.2022)
[2] https://battery-news.de/index.php/2021/03/16/neue-infos-zur-blade-battery-von-byd (Access 11.10.2022)
[cs 11.10.2022, 08.09.2023, 17.11.2025, 27.12.2025, 01,02.2026]
The business activity of Byton was already discontinued in 2021.
Byton was a Chinese BEV start-Up founded in 2017 by former BMW and Nissan managers in Honk-Kong, the first vehicle prototype was presented in 2018. Production of the first model, M-Byte, was scheduled to start in 2019, but was delayed several times due to financial difficulties.
In 2021, Byton was insolvent, and Byton has since ceased operations completely [1].
Sources
[1] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Byton_(company) (Access 27.10.2022)
[cs 27.10.2022]
Canoo’s business model, which was based on a platform concept, proved to be unsustainable. In January 2025, due to insufficient sales, the company filed for Chapter 7 bankruptcy, followed by liquidation.
Canoo was founded in 2017 under the name Evelozcity and was a US manufacturer of battery electric vehicles, most recently based in Bentonville, Arkansas. The company addressed the market segment for commercial and delivery vehicles as well as vans based on a modular multi-purpose platform (MPP) that combined the battery, drive, and control technology in a flat skateboard concept.

BEV platform from CANOO
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of Canoo Technologies Inc. [Press Release])

Van based on CANOO platform
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of Canoo Technologies Inc. [Press Release])
In 2023, only around 22 vehicles were delivered, which was also reflected in very low annual sales of around US$886,000. The company had originally forecast sales of between $50 million and $100 million for 2024, but in fact only achieved a very low single-digit million amount; at the same time, deliveries remained extremely low at less than a dozen vehicles.
[cs 16.10.2022, 18.02.2023, 05.12.2025]
Ceer is a New-Country start-up new-country start-up from Saudi Arabia and also the first Saudi Arabian car brand [1]. The company was founded at the end of 2022 as a joint venture between the state-owned Public Investment Fund (PIF) and Taiwanese electronics manufacturer Foxconn. The brand is positioning itself as a pioneer of a new Saudi automotive industry as part of Vision 2030 and plans to offer battery-electric vehicles – including sedans and SUVs – for the domestic market, the Gulf region, and the wider Middle East.
Ceer is building a production facility in King Abdullah Economic City (KAEC) near Jeddah; the site is expected to cover more than one million square meters. The contract for the plant has been awarded, and construction began in early 2023.
International technology partnerships are an integral part of the concept: Ceer uses licensed components from German manufacturer BMW and drive systems from Croatian start-up Rimac Technology. The company has also signed a supply contract with Hyundai Transys for e-drive systems for the electric platform. Foxconn is responsible for the electronic architecture, infotainment, and connectivity. The first series delivery was originally scheduled for 2025, but this has since been postponed to 2026 [2].
Technologically, Ceer is a very ambitious project, but it has extremely financially strong investors.
Sources
[1] https://ceermotors.com/ (Homepage, Access 14.02.2023)
[2] https://ceermotors.com/news/ceer-to-establish-electric-vehicle-manufacturing-site-at-king-abdullah-economic-city/ (Access 14.02.2023)
[cs 14.02.2023, 06.12.2025]
Cenntro is a U.S. startup based in New Jersey for small and medium-sized battery–electric VANs that can be used primarily for inner-city logistics. In 2021, a merger with Naked Brand Group took place.
In 2022, Cenntro acquired a majority stake in Tropos, a company based in Herne, Germany, which is active in the same market segment..

Cenntro Mini-Van Metro
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of Cenntro Electric Group Limited [Homepage])
Cenntro’s first product is the Metro van, of which more than 3300 units have been produced since 2017; target markets are Europe, the USA, Japan, Korea, Singapore and Israel. The product range has now grown significantly, and Cenntro now covers payloads from 500 kg (Logistar 100 model) to 3500 kg (Logistar 400 model).
LFP cells are used in the HV battery, although classic lithium-ion cells with NMC chemistry are still installed in the Metro. The cell supplier of Cenntro of the editorial office is not known.
A separate subsidiary for battery production was established in August 2022, the production site is Monterrey in Mexico, and production is scheduled to start in 2023.
Since the merger with Naked Brand Group, Cenntro is listed on Nasdaq (ISIN AU0000198582, WKN A3DAKM) [1].
Sources
[1] https://ir.cenntroauto.com/ (Access 15.02.2023)
[cs 16.10.2022,, 15.02.2023]
Car manufacturer with cult status, as the only internal combustion model with gullwing doors produced only between 1981 and 1982 played a leading role in the Hollywood trilogy “Back to the Future“. In business terms, the company was a flop; demand collapsed relatively quickly after massive quality problems.
However, the few vehicles still on the road today are always a crowd puller at classic car events.

Delorean model ALPHA5
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of DeLorean Motors Reimagined LLC [Homepage])
A BEV start-Up is now venturing a new edition as a BEV model called ALPHA5, which is also set to feature the iconic gullwing doors. However, many details remain unclear: neither the price nor the start of series production have been specified, and there are doubts as to whether the ambitious plans announced are realistic.
It therefore remains to be seen whether this cult brand’s second attempt will be more successful.
Sources
[1] https://delorean.com/ (Homepage, Access 19.10.2022)
[cs 19.10.2022, 12.12.2025]
Deepal is a new BEV brand from the Chinese state-owned automotive company Changan. Changan itself was founded in 1862 and ranks third in terms of sales in 2025 among the four major state-owned car manufacturers.
Deepal operates as an independent new energy brand under the control of Changan Automobile (Changan holds a ~50.99% stake), alongside other brands in the group such as Changan itself, Avatr, and Nevo. The vehicle range includes sedan and SUV models, which are available as BEV variants or range extenders.
Sales began in 2022, and sales figures have risen significantly since then:
- In 2023, just under 137,000 vehicles were sold.
- In 2024, sales rose to around 240,000 units.
- For 2025, sales are estimated at 300,000 to 350,000 vehicles.
Deepal is not yet profitable, but has been able to gradually reduce its losses:
- In 2023, revenue was RMB 26.9B (≈ € 3.5B) and the net loss was around RMB 3.1B (≈ € 0.4B).
- In 2024, revenue rose to RMB 37.2B (≈ € 4.8B) and losses were reduced to RMB 1.6B (≈ € 0.2B).
- For 2025, revenue is estimated at around RMB 50B (≈ € 6.5B) and the loss at RMB 1.5B (≈ € 0.2B).
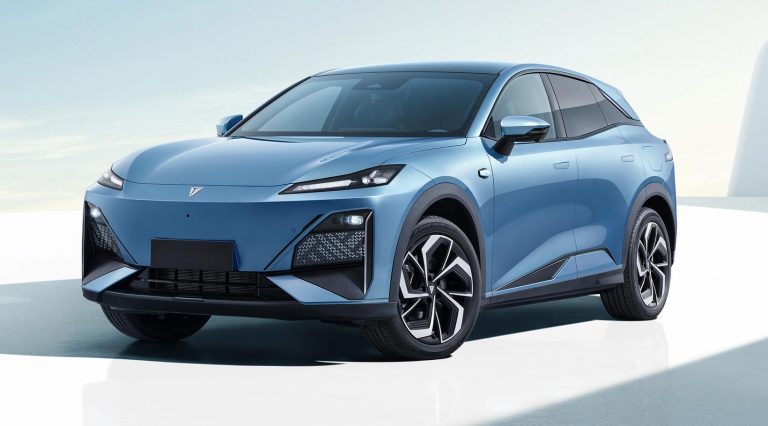

Deepal model S07
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of CHANGAN [Homepage])
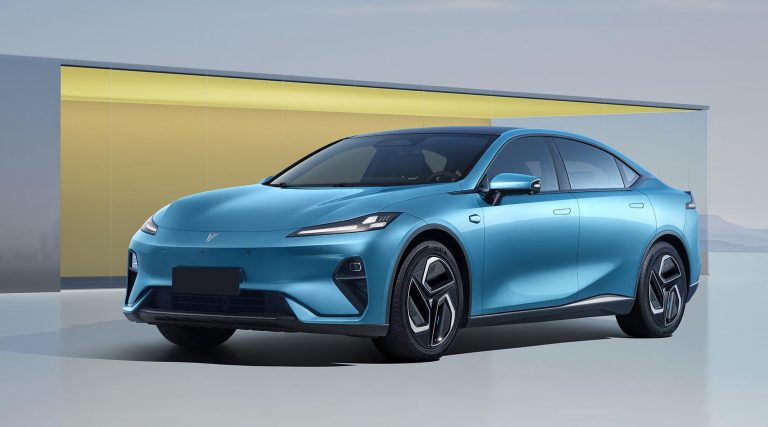

Deepal model L07
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of CHANGAN [Homepage])
Deepal primarily sources its cells from CATL. Delivery is carried out both through traditional supply contracts and through a joint venture between Changan and CATL. Depending on the model and market, LFP and NMC cells are used.
At the same time, Deepal is working within the Changan Group to achieve greater vertical integration of battery value creation, including its own cell technologies (such as high-load 4C cells and, in the future, semi-solid and solid-state batteries).
Sources
[1] https://www.globalchangan.com/deepal.html (Access 23.02.2026)
[cs 23.02.2026]
Evergrande New Energy Auto [↑] [↓] [⇑] [⇓]
Evergrande is one of the largest Chinese real estate companies, which has made the headlines due to its debt crisis [1]. With the new business division and the new BEV brand Evergrande New Energy Auto, the company wanted to tap into new sources of revenue.
The goals communicated by Evergrande sounded extremely ambitious. By 2025, production was to be ramped up to one million electric vehicles per year, and by 2035, five million electric vehicles were planned [2]. The company started production of the model Hengchi 5 in September 2022, with deliveries scheduled to begin in October; the Hengchi 6 and 7 were to follow successively in 2023.
However, developments did not go as hoped: production of the Hengchi 5 was discontinued at the end of 2022 due to lack of demand. In the years that followed, the economic situation deteriorated dramatically. In the summer of 2024, a Chinese court ordered the bankruptcy of two subsidiaries of the EV division.
Despite the tense situation, the bankruptcy administrators have been actively seeking to sell shares in the company since 2024: a preliminary agreement was in place with a potential investor. However, by early 2025, it became apparent that no binding strategic buyer had been found. Although offers are still being reviewed, a secure rescue deal seems highly unlikely.
Evergrande New Energy Auto is listed on the stock exchange, including in Frankfurt (ISIN HK0000264595, WKN A14Y51); however, trading has been suspended.
Sources
[1] https://www.faz.net/aktuell/finanzen/staat-eilt-krisenkonzern-china-evergrande-zu-hilfe-17748055.html (Access 27.10.2022)
[2] https://mobilesite.evergrande.com/en/business.aspx?tags=6 (Homepage, Access 27.10.2022)
[cs 27.10.2022, 21.02.2023, 07.12.2025]
EVUM Motors GmbH is a spin-off of the Technical University of Munich and is developing a compact, electrically powered small van with all-wheel drive under the name EVUM aCar. The company is currently under compulsory administration by an insolvency administrator.
Since its founding in 2017, the company has pursued the goal of bringing the aCar, a robust, simple, and flexible electric commercial vehicle for agriculture, trade, municipalities, and transport, to market. After switching to series production, the first vehicles were delivered in the summer of 2021; production took place at the Bayerbach site near Ergoldsbach.
The aCar concept is based on a simple, cost-conscious design with a 48-volt drive, which allows the vehicle to be charged from a standard 230-volt outlet and provides a range of up to 200 km and a payload of up to 1000 kg. EVUM Motors thus targeted customers looking for an affordable, versatile, and low-maintenance transport vehicle — originally with an eye on emerging markets and rural regions, but later also with a focus on Europe.

EVUM aCar
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of Evum Motors GmbH [Download Area])
Despite multiple rounds of financing and support from investors and institutional funding, EVUM Motors appeared to be struggling with significant economic problems. On April 30, 2025, the competent Munich District Court ordered provisional insolvency administration of the assets of EVUM Motors GmbH; an insolvency administrator was appointed. Business operations involving development and production are to be continued, at least for the time being.
This means that EVUM Motors is currently no longer in a position to pursue its original corporate goals. It remains to be seen whether restructuring or the entry of investors will be successful.
Sources
[1] https://evum-motors.com/ (Access 18.02.2023)
[cs 18.02.2023, 07.12.2025]
Faraday Future [↑] [↓] [⇑] [⇓]
Faraday Future was founded in 2014 in California as a BEV start-up, being a joint American-Chinese project. The company has locations in Los Angeles (headquarters and R&D center), Silicon Valley, and China (Beijing, Shanghai, and Chengdu) [1].
The first model is a luxury SUV called FF91, which the company says will compete with premium brands such as Bentley, Ferrari, Maybach, and Rolls-Royce. The few known technical specifications include an output of 1050 hp, acceleration from 0 to 100 km/h in 2.3 s, and a range of about 600 km.
In reality, however, economic success has failed to materialize: according to available data, Faraday Future had brought only a very small number of electric vehicles to market by mid-2025. Officially, not even 20 vehicles had been sold in eleven years. Production thus barely exceeded small series. There have been repeated reports of significant financing problems that have been weighing on the company for years.

Faraday Future model FF91
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of Faraday&Future Inc. [Press Room])

Interieur F91
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of Faraday&Future Inc. [Press Room])
Most recently, Faraday Future reported an operating loss of approximately $27.4 million for the second quarter of 2025 and a monthly cash burn rate of approximately $9 million. Although cash reserves temporarily reached an 18-month high, this improvement cannot hide the fact that the business model is characterized by uncertainty.
As a result of ongoing problems, Faraday Future is attempting to counteract these with alternative strategies, including restructuring, partnerships, and diversification of the company’s activities. Whether these measures will be sufficient to stabilize the company in the long term and achieve its original goals remains to be seen.
Sources
[1] https://www.ff.com/(Homepage, Access 18.02.2023)
[cs 27.10.2022, 07.12.2025]
The Fisker Inc. filed for bankruptcy in June 2024, liquidation was confirmed by the court in fall 2024, and the company was subsequently wound up completely. Production, sales, and all planned model series were discontinued, and the brand no longer exists operationally. Remaining assets are merely being liquidated, and there are currently no plans to continue the company.
Back in 2007, former BMW designer Hendrik Fisker had already founded a BEV start-up under a similar name. The first model was a plug-in hybrid that was unveiled at the Detroit Auto Show in 2008. Due in part to the bankruptcy of cell supplier A123, production had to be discontinued again in 2012 and the assets were sold to a Chinese group of companies.
In 2016, the company was re-established under the name Fisker Inc., but now with a focus on battery electric vehicles (BEVs). The first model was an SUV called Ocean, which can be optionally equipped with solar cells on the roof. The Fisker Ocean electric SUV was the first series-production vehicle to be offered, manufactured by contract manufacturer Magna Steyr in Graz. At the same time, Fisker planned further models such as the compact crossover SUV Fisker Pear and the Fisker Alaska pickup truck.

Fisker Ocean – Exterieur
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of Fisker, Inc.. [Press Gallery])

Fisker Ocean – Interieur
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of Fisker, Inc.. [Press Gallery])
However, the economic reality was disappointing, with financial difficulties already apparent by the end of 2023. In March 2024, the company announced that it would not be viable without fresh capital.
Parallel to these developments, the Ocean suffered from technical problems and several recalls — further undermining confidence among customers and suppliers. The ambitious expansion plans with Pear and Alaska came to a standstill: production of the Ocean was discontinued and the future of the brand projects is currently uncertain.
Talks with potential partners, including an automobile manufacturer, were unsuccessful, and trading in the company’s shares was soon suspended and its stock market listing revoked. In June 2024, Fisker finally filed for creditor protection under US bankruptcy law (Chapter 11).
Sources
[1] https://www.fiskerinc.com/ (Homepage, Access 21.02.2023)
[cs 21.02.2023, 07.12.2025]
GAC Aion was established in July 2017 as a new BEV brand of GAC Group (Guangzhou Automobile Group Co., Ltd.) focusing on innovative battery electric vehicles. GAC Group is a state-owned enterprise from 1954, currently it is the fifth largest Chinese automaker of internal combustion engine vehicles [1].
Since November 2025, GAC Aion has also entered into the production of range extender models (EREV/REEV), initially with the Aion i60, a mid-size SUV that is available as a pure BEV variant as well as a range-extended version. Previously, the brand’s portfolio was entirely focused on battery electric vehicles.
The highest-volume BEV models include the Aion Y (compact crossover/SUV), the Aion S and S Plus (mid-size sedan), the Aion V (compact to mid-size SUV), and newer series such as the Aion RT (mid-size sedan) and the Aion UT (compact hatchback). These models clearly form the sales focus. Accordingly, the REEV share in 2025 was expected to be only around 2%, while pure BEVs accounted for around 98% of sales.
GAC Aion got off to a very successful start. Sales figures rose significantly until 2023, but then fell again:
- In 2022, just over 271,000 units were delivered.
- In 2023, there was a significant increase to over 480,000 vehicles.
- In 2024, sales fell to just under 375,000 units.
- A further decline to around 286,000 vehicles is expected in 2025.
The financial figures for GAC Aion are not reported separately. The GAC Group remained profitable until 2024 but experienced a significant decline in earnings, largely due to weaker performance in the internal combustion engine business and its joint ventures:
- In 2023, revenue amounted to nearly RMB 130B (≈ € 16.6B), while net profit totaled approximately RMB 4.43B (≈ € 0.57B).
- In 2024, revenue declined to nearly RMB 107.8B (≈ € 13.8B), and profit fell to around RMB 0.82B (≈ € 0.11B).
- In 2025, revenue is expected to decrease to about RMB 100B (≈ € 12.2B); for the full year, a net loss of approximately RMB 1.8–2.6B (≈ € 0.23–0.33B) is anticipated.
However, the BEV segment, particularly GAC Aion, which is burdened by high investments, price pressure, and low margins, is not the main driver of the decline in earnings; this is primarily due to the weakness of the combustion engine business.

GAC Aion Hyper GT – Exterieur
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of GAC Aion New Energy Automobile Co., Ltd. [Press Gallery])

GAC Aion Hyper GT – Interieur
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of GAC Aion New Energy Automobile Co., Ltd. [Homepage])
Models on offer include classic sedans (AION S, AION S Plus) and SUVs (AION LX Plus, AION V Plus, AION Y Plus). AION attracted particular attention with the Hyper GT, a four-door super sports car with a drag coefficient of 0.19 cW; production and sales are scheduled to start in 2023. No export to Europe is known [4].
Parallel to production in its home market of China, GAC Aion prepared for its market entry in Europe in 2025: The official launch for the European market was announced at IAA Mobility 2025 with the Aion V model, with deliveries initially to Poland, Portugal, and Finland, among other countries. In addition, assembly of Aion V SUVs began in December 2025 with partner Magna at the plant in Graz, Austria — a step with which GAC aims to avoid customs duties and drive forward its European expansion.
GAC Aion primarily sources its lithium-ion batteries from CALB, CATL und Farasis Energy, with CALB accounting for over 70% of the total. In newer models such as the Aion UT Super, GAC Aion is increasingly relying on CATL batteries, including CATL’s “Choco-SEB” swapping technology.
The parent company GAC Motor is listed on the stock exchange (ISIN CNE100000Q35, WKN A1C2W3).
Sources
[1] https://www.gac.com.cn/en/brand (Access 22.02.2023)
[cs 22.02.2023, 08.12.2025]
Galaxy was introduced in 2023 as a new NEV brand within the Geely Holding Group. Unlike Polestar, Galaxy did not originate from an independent company, but was established directly as a strategic electrification brand by Geely Auto. Today, Galaxy is the Geely Group’s most successful NEV brand, focusing on plug-in hybrid (PHEV) and battery electric vehicles (BEV) for the Chinese domestic market. The brand is an integral part of the group-wide electrification strategy and complements higher-positioned sister brands such as Zeekr.
Geely does not provide an official breakdown by drive type for the Galaxy brand, but based on the published model figures, a clear trend can be seen for 2025. Pure BEVs are expected to account for the majority of sales, at around 60 to 70 percent, while plug-in hybrids will account for around 30 to 40 percent. EREV models do not yet play a role, as such vehicles are not expected to be on the market until 2026.
The first model was the Geely Galaxy L7 SUV, a plug-in hybrid. This was followed shortly afterwards by other electrified models such as the Geely Galaxy L6 sedan and the Geely Galaxy E8 battery electric series.
Geely is currently by far the most dynamic NEV brand, with sales figures exceeding the million mark after just two years:
- In 2023, just under 83,500 vehicles were delivered.
- In 2024, the figure was already almost 495,000 units.
- In 2025, sales jumped to 1,240,000 vehicles.
Unlike independently listed brands, no separate financial figures are published for Galaxy. Its economic performance is included directly in the overall balance sheet of Geely Auto, whose NEV division has grown strongly in recent years and now accounts for a significant share of the group’s sales.

Geely Galaxy E5 – Exterieur
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of Geely Auto [Press Release])

Geely Galaxy E5 – Interieur
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of Geely Auto [Press Release])
The Galaxy models are not only sold in China, but have also been developed for foreign markets: The compact SUV Galaxy E5 (marketed outside China as the Geely EX5) was developed with both left-hand and right-hand drive versions from the outset and was presented at Automechanika in Frankfurt in 2024, with confirmed sales and registration plans in Europe, Australia, Southeast Asia, and other regions such as Norway, Thailand, and Indonesia.
Sales of the EX5 began in selected European markets (including Germany and the UK) in 2025, and the vehicle is also available in South Africa and Australia/New Zealand. In addition, Geely recorded NEV exports in regions such as Pan-Europe, Latin America, Africa, and Asia-Pacific with several tens of thousands of units, with around 36,000 pure electric NEVs exported during the year.
Galaxy relies on the group’s own LFP-based battery technology (Aegis Short Blade) for its BEV models (e.g., Galaxy E5/EX5). In contrast to its sister brands Polestar and Zeekr, there are no indications of external cell suppliers.
Zhejiang Geely Holding Group itself is not publicly traded but is privately owned by founder Li Shufu and his associates. However, its subsidiary Geely Automobile Holdings Ltd. is listed on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange and bundles the group’s passenger car business. This gives Geely access to the capital market, but the holding structure remains privately organized.
Sources
[1] https://global.geely.com/en/ (Access 03.03.2026)
[cs 03.03.2026]
Hozon Auto (Neta) [↑] [↓] [⇑] [⇓]
The Chinese BEV Start-up Hozon Auto filed for bankruptcy in June 2025.
The company was founded in 2014 in Zhejiang Province, south of Shanghai [1]; in addition, a research center for autonomous driving was opened in Silicon Valley in 2018 and a design center in Beijing in 2019 [2][3]. Since November 2021, cell and battery manufacturer CATL has held a stake in the subsidiary Neta Auto [4].
The products were sold in China under the Neta brand. The Neta V model ranked ninth on the list of the world’s best-selling electric cars in 2022 with around 94,400 vehicles sold.
Sales increased to 127,500 units in 2023, however sales figures declined significantly in subsequent years. In 2024, deliveries fell to just under 87,500 vehicles in 2024. At the same time, Neta recorded around 30,000 vehicles sold or exported abroad in 2024, and its sales partner network was expanded to 184 channels worldwide. The company announced its intention to significantly expand its export activities in 2025.

Hozon Auto Neta U2 – Exterieur
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of Hozon New Energy Automobile Co.,Ltd.. [Press Gallery])

Hozon Auto Neta U2 – Interieur
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of Hozon New Energy Automobile Co.,Ltd.. [Press Gallery])
However, as a result of declining sales in its domestic market, Hozon Auto’s economic situation has deteriorated dramatically: in 2023, the company reported revenue of RMB 13.554 billion (~€1.65 billion) and a net loss of RMB 6.758 billion (~€0.84 billion). Total assets were reported at RMB 21.366 billion (~€2.6 billion).
In January 2025, new registrations slumped sharply compared to the previous year, with fewer than 400 vehicles sold in February 2025. Accordingly, Hozon Auto filed for bankruptcy in June 2025.
Sources
[1] https://carnewschina.com/2017/04/28/hozon-auto-another-new-ev-brand-china (Access 24.03.2023)
[2] https://www.futurecar.com/2163/HOZON-Auto-Launches-R&D-Center-in-Silicon-Valley-to-Explore-Autonomous-Driving (Access 24.02.2023)
[3] http://www.chinadaily.com.cn/a/201904/01/WS5ca18428a3104842260b3ad3.html (Access 24.02.2023)
[4] https://www.electrive.net/2021/11/15/catl-beteiligt-sich-an-e-auto-marke-neta (Access 24.02.2023)
[cs 24.02.2023, 13.09.2023, 08.12.2025]
Human Horizons [↑] [↓] [⇑] [⇓]
The Chinese BEV start-up Human Horizons has been in formal insolvency proceedings or judicial restructuring since mid-2024 after the company was no longer able to meet its financial obligations.
Human Horizons was founded in Shanghai in 2017 by former GM China manager Ding Lei [1]. The company operated a production and assembly plant in Yancheng (Jiangsu) and a parts factory in Jinqiao, Shanghai. The HiPhi brand was launched in 2019.
In its early years, HiPhi positioned itself in the high-priced premium electric vehicle segment. The HiPhi X was the first production model, followed by the sporty HiPhi Z and the more affordable HiPhi Y, which was introduced in 2023. Despite technologically sophisticated products, the economic situation deteriorated significantly from 2023 onwards.
Only 226 HiPhi X vehicles were registered in 2023, and only 33 units in 2024; there are no reliable figures available for the HiPhi Y, but due to the production stoppage, similarly low volumes can be assumed. From 2025 onwards, there will be virtually no sales, as all operations will have been discontinued beforehand. Even the export plans to Europe, which began in 2023 with showrooms in Munich and Oslo, did not result in any verifiable sales volumes.

HiPHi X from Human Horizons
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of Human Horizons (Shanghai) Connectivity Technology Co., Ltd. [Media Center])

HiPHi Z from Human Horizons
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of Human Horizons (Shanghai) Connectivity Technology Co., Ltd. [Media Center])
In 2025, an attempt was made to reposition the HiPhi brand. Despite these measures, the company’s future remains uncertain, as the Chinese market is characterized by intense competition and a sharp decline in prices, and the brand has suffered a significant loss of confidence due to the production stoppage and bankruptcy.
Sources
[1] https://www.bloomberg.com/news/videos/2018-11-23/human-horizons-founder-ding-lei-on-tesla-video (Access 27.02.2023)
[cs 27.02.2023, 13.09.2023, 12.12.2025]
Hycan was a new new BEV brand launched in 2018 as a joint venture between GAC and NIO. Due to a lack of commercial success, business operations have now been suspended and, according to GAC Group, customer service has been wound up in an orderly manner.
GAC stands for Guangzhou Automobile Group, which is the fifth-largest Chinese manufacturer of combustion engine vehicles. It was founded in 1954 as a state-owned enterprise. NIO had withdrawn from the joint venture, meaning that Hycan was a GAC-only brand [1].
Sales of the first vehicles began in China in 2020. The models include the electric crossover Hycan 007, the compact model Z03, the mid-size sedan A06, and, since the end of 2023, the spacious MPV Hycan V09 [2].
Hycan has already experienced significant sales difficulties in recent years. Total sales for 2023 are reported to be only 18,559 vehicles, which is already a decline compared to 2022. Sales remained low in 2024; quarterly and monthly data and reports indicate that fewer than 20,000 units were sold in 2024.

Hycan 007 – Exterieur
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of Hechuang Automotive Technology Co., Ltd. [Homepage])

Hycan 007 – Interieur
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of Hechuang Automotive Technology Co., Ltd. [Homepage])
There are no reliable overall sales figures for 2025 available yet; individual monthly figures (e.g., September 2025) show only a few dozen units for V09, and figures for 2024 or 2025 on revenue, assets, and profit/loss are not publicly available.
According to the current public presentation, Hycan is “substantially defunct,” meaning that its operational business is dormant and the brand no longer exists de facto. According to the GAC Group, the takeover of customer service and the remaining structure was dissolved in an orderly manner.
Sources
[1] https://autonews.gasgoo.com/china_news/70021139.html (Access 07.06.2023)
[4] https://www.hycan.com.cn/ (Zugriff 26.05.2023)
[cs 26.05.2023, 07.06.2023, 12.12.2025]
IM Motors is a very young BEV joint-venture founded in January 2021 as a collaboration between SAIC Motors and Alibaba; the company targets the premium segment of Chinese electric vehicles [1][2]. Similar to Afeela and Aito, IM Motors is about combining the expertise of a traditional combustion engine manufacturer with an electronics group.
In 2024, CATL acquired a stake in IM Motors as part of a capital increase.
SAIC Motor itself (Shanghai Automotive Industry Corporation) is China’s largest automotive group; the company is state-controlled and sold around 4.740 million vehicles worldwide in 2024. In addition to its own brands, SAIC also produces vehicles for Western manufacturers, including VW and GM, as part of joint ventures.
The ADP (Advanced Digitized Platform) electric platform, jointly developed by SAIC and IM, is already being used by Audi for the new China-exclusive “AUDI” brand, which deliberately dispenses with the traditional four-ring logo. The first model of this brand had a successful launch in 2025 with over 10,000 pre-orders.
IM Motors has been offering its own production-ready vehicles since 2022 and will expand its market presence with SUVs and sedans starting in 2023. Sales figures show growth, but at a still low level. 38,250 vehicles were reported for 2023, and the number rose to 65,500 units for 2024.
No reliable total sales figures are available for 2025 as yet.

IM Motors LS7 IM – Exterieur
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of Zhiji Automobile Technology Co., Ltd. [Homepage])

IM Motors LS7 IM – Interieur
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of Zhiji Automobile Technology Co., Ltd. [Homepage])
In 2025, the portfolio was expanded with the introduction of the large IM LS9 SUV with range extender drive and a combined range of up to 1,500 km (with a 66 kWh battery). The LS9 is positioned as the brand’s new premium flagship.
No reliable data is available on exports to Europe or detailed sales figures outside China, which means that IM Motors appears to continue to focus on its home market in China.
CATL is named as the cell manufacturer for the batteries in IM models, including the battery in the new LS9.
Sources
[1] https://equalocean.com/company/zhijiqiche (Access 27.02.2023)
[2] https://www.immotors.com/ (Homepage, Access 27.02.2023)
[cs 27.02.2023, 04.06.2023, 01.08.2023, 12.12.2025]
Ineos Automotive [↑] [↓] [⇑] [⇓]
Ineos Automotive is a classic start-up, founded in 2018 in response to the discontinuation of the Land Rover Defender by Jim Ratcliffe, founder and CEO of the chemical company Ineos. Ratcliffe is an experienced adventurer who regularly undertakes challenging global expeditions in off-road vehicles, which explains the company’s focus on robust off-road models.
Together with Magna, a robust combustion engine off-road vehicle called the Grenadier was developed, which has been produced at the former Smart plant in Hambach, France, since 2022. Many components of the Grenadier, such as the engines, come from BMW.
The model range was later expanded to include the Grenadier Quartermaster pickup truck, while the Fusilier electric SUV, originally planned for 2026, was discontinued in 2024 due to economic and structural difficulties.

Ineos Grenadier
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of INEOS Capital Limited [Homepage])
The following months saw considerable operational pressures: production interruptions due to insolvent suppliers, a major recall of over 7,000 Grenadier vehicles in the US, rising costs, and a challenging market led to financial bottlenecks and extensive job cuts in 2025.
Although no official insolvency was announced, the restructuring measures and withdrawal from electric vehicle development indicate a clear crisis situation.
Sources
[1] https://www.ineos.com/businesses/ineos-automotive/ (Access 02.05.2023)
[cs 02.05.2023, 12.12.2025]
Izera is the BEV brand of a Polish New-Country start-up founded in 2016 by the state-owned consortium ElectroMobility Poland (EMP) [1]. According to the state supervisory authority, the project had suffered significant delays by 2023, prompting the Polish government to halt the project at the end of 2024 and dissolve the Izera brand. This brought an end to the ambitious plan to establish an independent Polish electric car for the mass market.
In 2020, the first two fully electric models were unveiled, a hatchback sedan and an SUV, with the aim of going into series production in 2023. The vehicles were designed by the Italian firm Torino Design, which brought on board experienced designers such as the former Jaguar designer. The plan was to build a factory in Jaworzno in the Silesian Voivodeship, which would have created around 3,000 jobs.

Izera hatchback model – Exterieur
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of ElectroMobility Poland S.A. [For Media])

Izera hatchback model – Interieur
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of ElectroMobility Poland S.A. [Homepage])
The vehicles were to be offered with two battery variants (40 and 60 kWh), with a target range of around 400 km. The platform, batteries, and electric motors were to be purchased externally for the most part, with the aim of producing around 60 percent of the parts in Poland itself.
In November 2022, there was a press release regarding the licensing of the Sustainable Experience Architecture (SEA) from the Chinese Geely Group, which would have required a revision of the previous development models.
In 2023, however, it became apparent that the project had achieved only a fraction of its original goals. According to the balance sheet of the responsible state control authority, the project had achieved only about four percent of its planned milestones at that point. In December 2024, the Polish government decided to discontinue the project and dissolve the Izera brand.
Sources
[3] https://izera.com/ (Homepage, Access 28.02.2023)
[cs 28.02.2023, 13.12.2025]
Leapmotor is a BEV start-up founded in 2015 in the Chinese city of Hangzhou. In 2018, the announcement about the first artificial intelligence chip “Lingxin 01” developed in China, which is specifically designed for autonomous driving as well as other deep learning-based systems, attracted attention [1].
In October 2023, Stellantis made a strategic investment in Leapmotor, acquiring around 20% of the company’s shares for around €1.5 billion. This was followed in May 2024 by the establishment of a joint venture with the aim of expanding exports outside China. Sales began in nine European countries in September 2024 and have been gradually expanded since then.
In 2025, it was announced that FAW would also like to acquire a financial stake in Leapmotor, in addition to Stellantis. FAW itself is the second or third largest state-owned car manufacturer in China, depending on the ranking – sales vs. sales figures. FAW plans to acquire a minority stake of around 5% in Leapmotor, following in the footsteps of its competitors SAIC and Changan, which already cooperate with other Chinese BEV start-ups.
Sales were still around 43,100 vehicles in 2022, but increased significantly in subsequent years:
- In 2023, around 111,170 vehicles were delivered.
- In 2024, the figure was 294,000 units, which is almost a threefold increase.
- In 2025, sales doubled to 596,600 vehicles.
This puts Leapmotor well ahead of the start-ups NIO and Xpeng, which are much better known in Europe.Xpeng.
Like many other BEV startups, Leapmotor is not yet profitable, but is making significant progress toward that goal:
- In 2023, Leapmotor generated revenue of around RMB 16.7B (≈ € 2.3B) and reported a net loss of RMB 4.2B (≈ € 0.5B).
- In 2024, revenue rose to just under RMB 32.2B (≈ €4.4B), while the net loss was reduced to RMB 2.8B (≈ € 0.37B).
- In the first half of 2025, Leapmotor achieved revenue of just under RMB 24.3B (≈ € 3.3B) with a half-year net profit of around RMB 30M (≈ € 4 million), marking its first half-year profitability.

Leapmotor C0I – Exterieur
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of Zhejiang Leapmotor Technology Co.,Ltd [News Room])

Leapmotor C0I – Interieur
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of Zhejiang Leapmotor Technology Co.,Ltd [Homepage])
Leapmotor’s models now include several series: the 4-door compact model T03, the 2-door sports coupe S01, the mid-size SUV C11, and the mid-size sedan C01. Since 2024, the globally oriented C10 has been added to the portfolio – a mid-size SUV that is the first model to be developed specifically for international markets.
The Leapmotor C10 is available as both a pure electric SUV (BEV) and a plug-in hybrid with a range extender (REEV). This is Leapmotor’s response to the huge success of Li Auto with its range extender models. The C10 is not only sold in China, but is now also available throughout Europe—including through dealer networks associated with Stellantis, i.e., also for markets such as Germany, France, Spain, and other European countries.
Leapmotor was once again represented at the IAA Mobility 2025 in Munich, where it presented the global world premiere of the compact Leapmotor B05 model and the European sales launch of the Leapmotor B10.
According to reports, approximately 13,450 vehicles were sold in 11 European countries by the end of September 2025. Assuming that sales in the last three months (October–December) remain at least at the level of the previous months, Leapmotor could sell between 16,000 and 20,000 vehicles in total in Europe in 2025.
According to well-known sources, the T03 uses LFP (lithium iron phosphate) cells from three different suppliers: CATL, Gotion und SVOLT Energy.
CATL is explicitly mentioned for exported European versions. In models with the cell-to-chassis (CTC) concept, especially the C01, the battery housing is structurally integrated into the bodywork – however, the specific cell supplier is not disclosed. In addition, Leapmotor has started producing its own battery packs through its subsidiary Lingxiao Energy; the cells used for this come from CATL and other suppliers, among others.
Leapmotor is listed in China (ISIN CNE100005K77).
Sources
[1] https://www.leapmotor.net/ (Access 25.11.2025)
[2] https://autonews.gasgoo.com/china_news/70014765.html (Access 28.02.2023)
[cs 27.10.2022, 13.09.2023, 25.11.2025]
Lightyear is a Dutch solar car start-up that emerged from a student initiative at Eindhoven University of Technology, which participated in various solar vehicle competitions.
Based on the project experience, Lightyear – similar to Aptera and Sono Motors – wanted to develop an electric vehicle with solar panels that would generate part of the energy required for driving directly from the sun. This model, called Lightyear 0, was originally intended to be sold for €250,000, but after producing a few vehicles, Lightyear had to file for bankruptcy in January 2023 due to lack of demand [1].

Lightyear 02
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of Atlas Technologies B.V. [Press Area])
As a result of its insolvency, Lightyear changed its business model. Instead of building its own solar cars, the company is now focusing on developing and supplying solar panels for vehicles from other manufacturers. At the same time, there was a change in management in the hope that the company’s expertise in solar technology would enable it to operate more successfully in the market.
It remains to be seen whether this change in strategy will be successful in the long term.
Sources
[1] https://lightyear.one/ (Homepage, Access 02.03.2023)
[cs 02.03.2023, 13.12.2025]
Li Auto is a Chinese electric vehicle Start-up start-up founded in 2015 by Li Xiang, whose investors include ByteDance, a company made famous by TikTik.
Li Auto is one of the few companies that have so far exclusively produced so-called range extender models. The vehicles have an internal combustion engine on board, which is only used as an electricity generator. Unlike a parallel hybrid, there is no mechanical coupling of the combustion engine to the drive wheels [1].
Four SUV models have been developed so far, designated Li L7, Li L8, Li L9, and Li One, and marketed primarily as family vehicles. At 5 m long, the L7 is already slightly larger than a BMW X5, while the L9, at 5.22 m, towers over the X7 by several centimeters. In all models, the combustion engine for range extension is located in the rear of the vehicle.
Sales rose from around 32,500 vehicles in 2020 to over 133,000 units in 2022. This year, Li Auto surpassed its competitors NIO and Xpeng in annual delivery figures for the first time, establishing itself among the highest-volume Chinese NEV manufacturers.
Growth continued in the following two years, but slumped again in 2025:
- In 2023, 376,030 vehicles were delivered.
- In 2024, the figure was 500,508 units, an increase of 33% over the previous year.
- In 2025, sales fell significantly to around 406,000 vehicles, representing a decline of almost 20%.
The reasons for the decline in 2025 are increasing competition in the Chinese market, lower demand for range extender models, and recalls. However, Li Auto is one of the few BEV start-ups that became profitable relatively quickly after its founding:
- In 2023, net profit was RMB 11.8B (~€ 1.54B) on revenue of just under RMB 124B (~€ 17.4B).
- In 2024, net profit fell to just over RMB 8B (~€ 1B) with revenue rising to RMB 144.5B (~€ 19.3B).

Li L9 – Exterieur
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of Li Auto Inc. [Homepage])

Li L9 – Interieur
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of Li Auto Inc. [Homepage])
In addition to its range extender models, Li Auto has also entered the development and production of battery electric vehicles. The flagship BEV “Mega” and the models in the new i series (e.g., i8 and i6) use 800 V technology and large battery packs and are intended to broaden Li Auto’s long-term positioning. In 2024, Li Auto Inc. delivered around 10,800 BEV models, and an increase to around 120,000–150,000 pure electric vehicles is expected for 2025.
Li Auto sources its battery cells primarily from CATL. In addition, Li Auto established a 50:50 joint venture with Sunwoda in 2025 to develop and produce its own lithium-ion batteries.
In terms of export strategy, the focus remains clearly on the Chinese domestic market. Official exports on a larger scale to Europe or the US have not yet started; so far, there have mainly been parallel exports. Although Li Auto is slowly expanding its international presence – including an R&D center in Munich – a full-fledged market launch in Europe is still pending.
Li Motor is listed on the stock exchange, including Frankfurt (ISIN KYG5479M1050, WKN A2QACD).
Sources
[1] https://ir.lixiang.com/ (Homepage, Access 22.04.2023)
[cs 22.04.2023, 21.11.2025]
Liux is a Spanish BEV start-up founded in 2021 by David Sancho Domingo and Antonio Espinosa de los Monteros in Madrid [1]. The choice of name does not seem very fortunate, as it is close to a very popular operating system, which makes searching the Internet much more difficult.
Investors include the leasing provider OK Mobility and the Spanish Ministry of Industry, and further rounds of financing are required to implement series production [2].
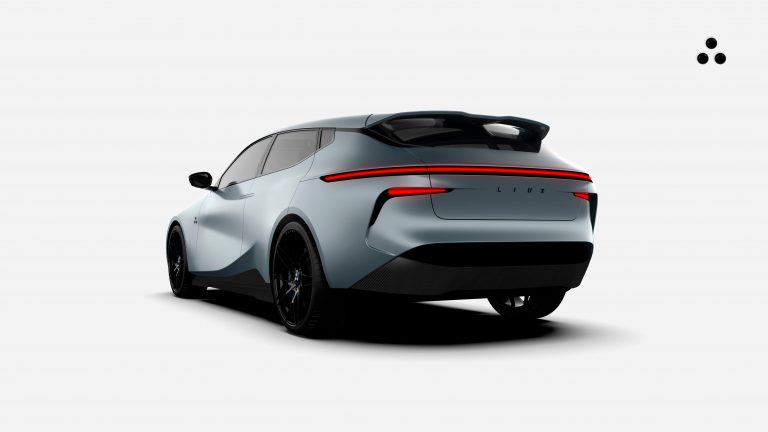

Liux prototype Animal
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of NATURAL MOVEMENT, S.L. [Press Gallery])

Liux prototype Gecko
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of NATURAL MOVEMENT, S.L. [Press Gallery])
The first prototype presented was the Animal model, a crossover between an SUV and a station wagon. Liux is now focusing on a 2-seater city vehicle called Gecko, which externally resembles the 1st generation Smart.
Liux emphasizes that particularly many components of the Animal will be made from renewable natural resins and natural fibers. The number of components is to be reduced by 25% compared with comparative vehicles.
Despite ambitious plans, Liux continues to face significant challenges. Although OK Ventures, the venture capital arm of the OK Group, came on board as the main investor in August 2024, providing fresh capital and strategic support, it remains unclear when series production will actually start.
At this point in time, it is therefore not clear whether Liux will be able to achieve the financial and production base necessary for economically viable production and market entry.
Sources
[1] https://www.liux.eco/ (Homepage, Access 02.03.2023)
[2] https://www.auto-motor-und-sport.de/verkehr/liux-animal-nachhaltige-e-autos-ab-2023 (Access 02.03.2023)
[cs 02.03.2023, 13.12.2025]
Lordstown Motors [↑] [↓] [⇑] [⇓]
Lordstown Motors is a BEV start-up that had to file for bankruptcy in June 2023; the company has already been dissolved.
Lordstown Motors was founded in 2018 by Steve Burns [1]. The following year, the company acquired the former GM plant in Lordsdown, Michigan, from General Motors. Due to financial difficulties, the plant was sold to Taiwanese contract manufacturer Foxconn for $230 million in November 2021 [2]. In November 2022, Foxconn invested another $170 million in Lordstown Motors [3].
Lordstown Motors had developed a typical American light truck called Endurance with a length of 5.8 m. The technical highlight of this model was that all four wheels were driven by a so-called wheel hub motor. The motor was located in the wheel hub directly on the tire, which significantly reduced the complexity of the powertrain components, as components such as drive shafts and differential gears were no longer necessary.
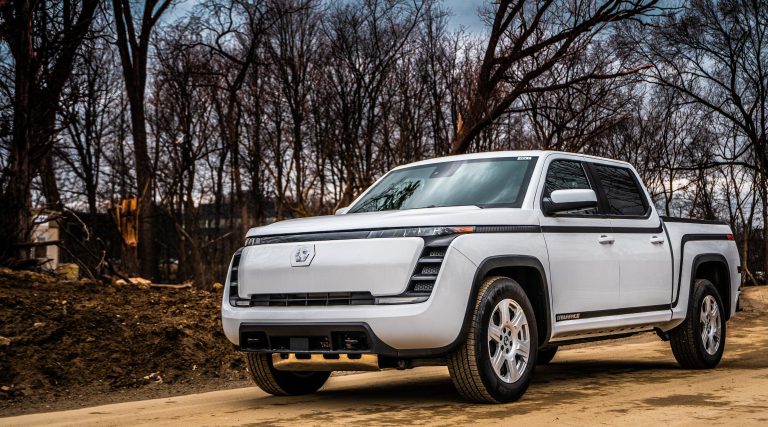

Endurance from Lordstown Motors – Front
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of Lordstown Motors Corp. [Media Page])
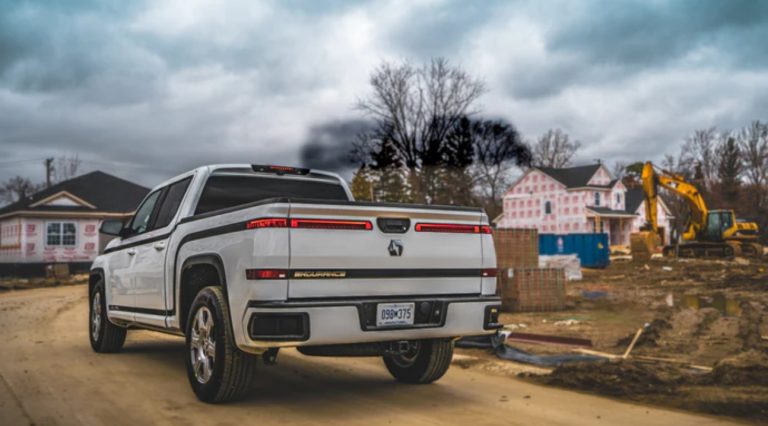

Endurance fromLordstown Motors – Back
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of Lordstown Motors Corp. [Media Page])
The disadvantage of this drive concept is the unsprung masses, which in the Endurance were approximately twice as high as in a comparable vehicle with a conventional powertrain due to the weight of the electric motor. In an interview, the founder and CEO Steve Burn explicitly confirmed that the development of the spring-damper system had been a major challenge [4].
After producing 31 vehicles, production was halted in February 2023 due to quality issues, with a well-known German car magazine already questioning the future of Lordstown Motors at that time [5].
The supplier for the electric motor was the Slovakian company Elaphe [6].
Sources
[1] https://www.carscoops.com/2019/12/lordstown-endurance-to-have-at-least-200-miles-of-range-and-four-electric-motors (Access 03.03.2023)
[2] https://investor.lordstownmotors.com/news-releases/news-release-details/foxconn-and-lordstown-motors-enter-transformative-strategic (Access, Zugriff 03.03.2023)
[3] https://investor.lordstownmotors.com/news-releases/news-release-details/lordstown-motors-and-foxconn-broaden-strategic-partnership (Access, Zugriff 03.03.2023)
[4] https://www.ideastream.org/news/economy/2020-06-29/lordstown-motors-big-gamble-on-hub-motors (Access 03.03.2023)
[5] https://www.auto-motor-und-sport.de/verkehr/hindenburg-research-lordstown-motors-iphone-hersteller-foxconn-werksverkauf (Access 03.03.2023)
[6] https://www.lordstownmotors.com/blogs/news/lordstown-motors-releases-business-updates-prepares-ohio-factory-to-begin-building-betas-next-month (Homepage, Access 03.03.2023)
[cs 03.03.2023, 06.08.2023, 13.12.205]
Lucid Motors was founded back in 2007 as a BEV start-up under a different name in California. Originally a supplier of BEV components such as battery and e-motor, it was renamed Lucid Motors in 2016. As part of this rebranding, the development of a luxury BEV vehicle was also announced, with the first prototype unveiled in December 2016. Welshman Peter Rawlinson, who was instrumental in the development of the Tesla Model S, joined Lucid as CTO in 2013 and became CEO in 2019 [1].
In a December 2022 equity offering, Lucid raised $1.5 billion, with $800 million coming from Saudi Arabian investors. In total, Saudi Arabian funds hold a stake of about 62%.
Lucid Motors follows the large-car-large-profit strategy, i.e. the first model Lucid Air is a luxury sedan with extreme performance data such more than 1000 hp, up to 883 km WLTP range and acceleration from 0 to 100 in 2.7 s. Lucid uses a 900 V architecture, which in particular also enables fast charging; a charging time of 15 min is specified for 400 km driving range [3].
In 2022, Lucid Motors has produced 7180 Air-type vehicles. Sales in Europe have also started, showrooms have been opened in Germany, Switzerland and the Netherlands, among other countries.
Lucid Motors achieved annual sales of $595.3 million in 2023; for 2024, the company reported sales of $807.8 million. In 2024, Lucid produced 9,029 vehicles and delivered a total of 10,241 vehicles. Delivery figures rose slightly in 2025, albeit from a low level; in the third quarter of 2025, the company delivered 4,078 vehicles.

Lucid Air – Exterieur
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of Lucid Group, Inc. [Media Room])

Lucid Air – Interieur
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of Lucid Group, Inc. [Media Room])
Due to the still very low number of units sold, Lucid continues to operate at a loss. In the third quarter of 2025, the net loss amounted to $978.4 million, which represents a slight decrease compared to the same period last year.
The Lucid Gravity is an SUV and Lucid Motors’ second model; series production began in Arizona at the end of 2024. According to industry figures, only nine Gravity SUVs were officially registered between January and June 2025, but Lucid says this does not reflect actual sales figures; the company itself claims to have sold several hundred units. The Gravity made its official debut in Europe at the IAA Mobility 2025 in Munich.
Delivery figures for Europe have been very low so far: according to reports, only 20 vehicles were newly registered in Germany in 2024, for example, and delivery figures across Europe were apparently in the low three-digit range.
Despite its high-quality drive and battery technology, Lucid faces major challenges in its transition from a niche manufacturer to higher production volumes. Although investor support secures financing in the short term, the company’s economic viability remains heavily dependent on whether Lucid can achieve significantly higher volumes at competitive costs in the medium term.
Lucent’s cell supplier is Panasonic [5].
Lucent is listed on the stock exchange, including in Frankfurt (ISIN US5494981039, WKN A3CVXG).
Sources
[1] https://www.businessinsider.de/wirtschaft/mobility/elon-musk-tesla-erfolgsgeheimnis-lucid-motors-air-chef-peter-rawlinson-unermuedlicher-optimismus (Access 04.03.2023)
[2] https://www.cnbc.com/2022/12/19/ev-maker-lucid-raises-from-the-saudi-public-wealth-fund-and-other-investors.html (Access 04.03.2023)
[3] https://www.lucidmotors.com/ (Homepage, Access 04.03.2023)
[4] https://www.lucidmotors.com/de-de/media-room/panasonic-agreement-supply-lithium-ion-batteries (Homepage, Access 04.03.2023)
[cs 04.03.2022, 13.12.2025]
Mullen Technologies [↑] [↓] [⇑] [⇓]
Mullen Technologies is a BEV start-up from California founded in 2012 by David Michery. It was difficult to identify a consistent corporate strategy in the company as it was originally founded. The models presented on the homepage were a hodgepodge of different vehicle categories such as sports cars, light trucks, trucks, vans, and SUVs [1].
As part of its strategic realignment, Mullen was merged with Bollinger Motors. The company now operates under the name Bollinger and focuses primarily on electric trucks for commercial use [2].
In the commercial vehicle sector, Bollinger focuses on battery-electric trucks in classes 1 to 5 for commercial use. The central model is the Bollinger B4, a fully electric Class 4 truck with a cab-over design, which belongs to the weight class of around 6.4 to 7.3 tons gross vehicle weight. The vehicle is designed for various commercial applications such as urban logistics, municipal fleets, and service vehicles, and is prepared for different body types.
In addition, the Bollinger B5 is a Class 5 truck that offers a higher payload with a gross vehicle weight of around 7.3 to 8.8 tons. The B5 is based on the same technical concept, but is aimed at more demanding applications in regional distribution transport as well as in the infrastructure and utilities sectors.
Actual sales figures for Bollinger trucks have remained limited to date. Although pre-orders and pilot projects with fleet customers have been announced, series deliveries are significantly below the originally announced expectations. Financial difficulties, production delays, and repeated restructuring have slowed the market ramp-up. Whether the truck activities can be established economically depends largely on stable demand and reliable series production.
Sources
[1] https://www.mullenusa.com/ (Access 09.03.2023)
[2] https://bollingerev.com/ (Zugriff 14.12.2025)
[cs 09.03.2023, 14.12.2025]
Munro Vehicles [↑] [↓] [⇑] [⇓]
Munro Vehicles is a Scottish BEV start-up founded in 2021 by Russ Peterson and Ross Anderson. The company specializes in electric all-wheel-drive vehicles and develops robust electric 4×4 vehicles for demanding working environments such as mining, rescue, defense, and off-road applications.
Munro Vehicles has positioned itself particularly well with its Series-M production model; the model range includes variants such as the M170 and the more powerful M280, which differ technically in terms of power, torque, and price, but are all based on robust LFP battery technology.
No detailed, officially confirmed sales figures are available for 2023, although Munro reported several pre-orders and initial series production. Only a few concrete deliveries are reported for 2024; according to the company, four vehicles were sold in 2024, with the order backlog growing steadily to reach a volume of around £17 million (over 240 vehicles) by mid-2025.
Complete year-end figures for 2025 are not yet available, but the growing order book indicates rising demand; specific delivery figures for 2025 have not yet been officially reported.

Munro Vehicles
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of ALL TERRAIN ALL ELECTRIC LTD [Homepage])
Official, audited financial figures such as revenue or profit/loss for 2024 and 2025 are not publicly available. The company received fresh capital of around £2 million in October 2025 to scale up production of the Series M and meet existing demand, indicating the need for further financing to expand production.
Munro Vehicles uses robust LFP cells, although the cell manufacturer is unknown.
Sources
[1] https://www.munro-ev.com/ (Access 14.12.2025)
[cs 10.03.2023, 14.12.2025]
NIO is a BEV start-up founded by William Li in Shanghai in 2014; investors include Baidu, Lenovo and Tencent. The product range includes SUVs and sedans; already since October 2022, some of the vehicles have also been exported to Europe.
In addition to Germany, its European target markets include the Netherlands, Denmark, Norway, and Sweden (as already established core markets). NIO also plans to expand its presence in Europe.
NIO has introduced two sub–brands: ONVO (formerly Alps) for the mid-price segment and Firefly (for the entry-level segment). The ONVO brand was launched in China in mid-2024, while Firefly will be launched in China in early 2025. Both brands are set to enter the European market in 2025 and will target a broader customer base in China and Europe in particular. The aim is to use the new brands to compete more directly with volume manufacturers such as Volkswagen, Toyota, and BYD.
Sales began in 2020 with around 43,700 vehicles and have risen steadily since then:
- In 2022, only around 122,500 units were delivered.
- In 2023, there was a slight increase to around 160,000 vehicles.
- In 2024, just under 222,000 units were delivered.
- In 2025, sales rose by a third to 326,000 units.
Despite rising sales figures and growing revenues, NIO is not yet profitable and is expected to continue to report significant losses in the years 2023 to 2025:
- In 2023, revenues were around RMB 55.6B (≈ € 7.1B), with a net loss of around RMB 22.0B (≈ € 2.8B).
- In 2024, rising to around RMB 65.7B (≈ € 8.4B). Nevertheless, losses could not be reduced, amounting to RMB 22.7B (≈ € 2.8B).
- For 2025, the quarterly figures point to an improvement in operations, but the company remains in the red. In the third quarter of 2025, NIO reported a net loss of around RMB 3.5 billion (≈ €0.48 billion). A negative annual result is therefore to be expected for 2025.

NIO ET7
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy NIO Deutschlang GmbH [Press Release])

Battery swapping station from NIO
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of NIO Deutschlang GmbH [Press Release])
One of the special features of NIO is the battery exchange concept, with which NIO currently has a unique selling point. In special exchange stations, empty batteries can be replaced by full batteries, with the exchange taking place fully automatically and in just 5 minutes.
NIO now operates over 3,500 battery swap stations in China, more than 1,000 of which are located along highways. These stations perform up to 100,000 battery swaps every day. The battery swap system (“Power Swap Station”) is considered a central component of NIO’s infrastructure strategy and is set to be expanded further.
Exchange stations are now also in operation in Germany, with EnBW coming on board as a cooperation partner. Of course, vehicles with exchange batteries can also be charged at normal charging stations, i.e. battery exchange is an additional charging option.
In addition to saving time, battery replacement offers other advantages:
- Battery capacity loss is no longer an issue for vehicle buyers.
- Battery capacity can be adapted to the required driving profile.
- Older, already manufactured vehicles can also benefit from technological advances in cell technology.
Nevertheless, it remains to be seen whether the “battery swap” concept can hold its own against classic, cable-based charging in the long term.
Currently, there is a great deal of research being conducted on fast charging, and investments are being made in the expansion of fast DC chargers, i.e. the time saved by replacing the battery will be reduced. In addition, the construction of the exchange stations involves costs that NIO will have to bear on its own.
The main supplier of battery cells for NIO is CATL, with whom the company has a strategic partnership for the further development of battery technologies and the expansion of the battery exchange network.
For its particularly high-energy 150 kWh battery packs, cells from specialist supplier WeLion were sourced using semi-solid-state technology; However, production of the 150 kWh pack was discontinued in 2025 after only a few hundred units due to low demand. Nevertheless, this example impressively demonstrates the potential of the battery replacement concept.
In addition, NIO is diversifying its cell procurement through other suppliers such as CALB and Sunwoda, the latter primarily for the Firefly sub-brand.
NIO is listed on the stock exchange, among others in Frankfurt (ISIN US62914V1061, WKN WKN A2N4PB).
Sources
[1] https://www.nio.com/de_DE (Homepage, Access 17.03.2023)
[cs 17.03.2023, 11.7.2024, 16.12.2025, 08.02.2026]
Olymp Cars was a BEV start-up from Austria that was founded as a joint project between the companies abo-drive and Modern Mobility GmbH, both of which operate in the fleet management sector [1].
The former official website www.olymp-cars.com is no longer accessible. Against this background, it can be assumed that Olymp Cars did not implement its original plans and is currently considered inactive. Whether financial difficulties, a lack of investors, or strategic reasons were decisive factors in this decision has not been officially communicated, but seems obvious given the lack of public presence.

Sketch SUV model ARES
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of OLYMP – Cars [Homepage])
In 2022, Olymp Cars announced plans to build a scalable electric vehicle platform, which would be used to produce the ARES SUV as well as other passenger car models and a van. The vehicles were intended to be battery-electric models, with production to be carried out by contract manufacturers and key components, including battery cells, to be sourced from external suppliers. However, beyond the concept presentations and announcements, no reliable information on prototypes, production sites, or a binding start of series production has been published.
Sources
[1] https://www.olymp-cars.com/ (Access 21.03.2023)
[2] https://ecomento.de/2022/05/30/olymp-cars-aus-oesterreich-plant-mehrere-elektroautos-und-wasserstoffantrieb (Access 21.03.2023)
[cs 21.03.2023, 17.12.2025]
Ora is a new BEV brand from the private Chinese vehicle manufacturer Great Wall Motors, whose parent company is one of the larger Chinese automobile manufacturers with around 1.23 million vehicles sold worldwide (2024).
Compared to corporations such as BYD, SAIC, and Geely, GWM ranks in the upper midfield of Chinese OEMs in terms of sales volume and revenue and is usually ranked fifth in industry overviews. Compared to corporations such as BYD, SAIC, and Geely, GWM ranks in the upper midfield of Chinese OEMs in terms of sales volume and revenue and is usually ranked fifth in industry overviews.
The first concept cars were presented in 2008, but production and sales on the domestic market did not start until 2018. The design is based on European vehicles; the front end resembles a VW Beetle, while the rear is reminiscent of a Fiat 500. ORA brand vehicles are classified as minicars in China [1].
ORA initially launched successfully as a new BEV brand of an internal combustion engine manufacturer, but sales declined sharply in 2024:
- In 2022, nearly 104,000 units were delivered.
- In 2023, sales increased slightly to more than 108,500 vehicles.
- In 2024, deliveries fell significantly to around 63,000 units.
- For 2025, sales are estimated at approximately 90,000 vehicles.

ORA Funky Cat – Exterieur
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of O! Automobile GmbH [Press Release])

ORA Funky Cat – Interieur
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of O! Automobile GmbH [Press Release])
In Europe, including Germany, sales figures for 2023 and 2024 also remained well below projections. In Germany, only around 2,500 to 3,000 Ora brand vehicles were newly registered in 2023, and in 2024, the volume fell to below 2,000 units. For the European market as a whole, sales in 2023 were below 10,000 vehicles, and in 2024 they were even lower. So far, there are no signs of a substantial increase for 2025.
Great Wall Motor does not publish separate financial figures for the Ora brand. However, declining sales and the group’s repeatedly adjusted European strategy, including structural changes in the European sales network, indicate economic pressure to adapt. Specific financial difficulties for the Ora brand have not been officially confirmed, but developments point to a reassessment of the market position and pricing strategy.
The battery contains LFP cells supplied by SVOLT, which also belongs to Great Wall Motors [2].
Sources
[1] https://www.ora-motor.de/ (Access 22.03.2023)
[2] https://autonews.gasgoo.com/china_news/70022048.html (Access 02.06.2023)
[cs 26.03.2023, 17.12.2025, 18.02.2026]
Polestar was originally founded in 2005 as a Swedish racing company. In 2015, it was sold, including trademark rights, to Volvo Car Corporation (Volvo’s passenger car division), which at that time already belonged to the Chinese Geely Group. Today, Polestar is a BEV-brand owned by a Geely-Volvo joint venture that focuses on sports cars. Polestar currently sells its vehicles in 28 countries.
The first model, Polestar 1, was a plug-in hybrid (PHEV); with Polestar 2, Polestar made the transition to purely battery-electric vehicles (BEV). In 2023/2024, the model portfolio was expanded with the Polestar 3 and Polestar 4 SUV models. The Polestar 5 is planned as a performance sedan on a standalone 800V platform; its market launch has been postponed several times and is now scheduled for the second half of the 2020s.
Sales figures recently stagnated in the mid five-digit range, but rose slightly in 2025:
- In 2022, around 50,000 units were delivered.
- In 2023, there was a slight increase to just under 52,800 vehicles.
- In 2024, sales fell to around 44,850 units.
- In 2025, sales rose to over 60,100 vehicles.
Sales figures are thus significantly lower than those of Chinese competitors and Geely’s sister brand Zeekr. However, Polestar uses BEV platforms from Volvo and Geely, which saves on development costs.
In general, sales volumes are still too low, which is also reflected in Polestar’s financial results:
- In 2023, revenue amounted to around $ 2.38B (≈ € 2.2B), while the net loss was approximately $ 1.17B (≈ € 1.1B).
- In 2024, revenue declined to around $ 2B (≈ € 1.85B), while the net loss increased to approximately $ 1.3B (≈ € 1.2B).
- For 2025, based on preliminary figures and analyst estimates, revenue of around $ 2.2–2.4B (≈ € 2.0–2.2B) is expected; the net loss is likely to amount to approximately $ 1.0–1.1B (≈ € 0.9–1.0B).

Polestar 2 BST edition 230
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of Polestar AB [Media Page])
Polestar 2 Interieur
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of Polestar AB [Homepage])
Sales also declined in Europe. While a total of around 25,000 vehicles were delivered in Europe in 2023, the volume fell noticeably in 2024. In Germany, new registrations stood at around 6,000 vehicles in 2023, falling to around 3,000 units in 2024. No significant increase is expected for 2025, although Polestar aims to regain market share with its new SUV models.
Polestar sources cells from two different suppliers. For the Polestar 2, it is CATL for the 82 kWh battery and LG Energy Solution for the 69 kWh battery; both cell suppliers are also used in the Polestar 3. The Polestar 4 is equipped with battery cells from CATL.
Polestar is listed on the Frankfurt stock exchange (ISIN US7311052010, WKN A3DP4R).
Sources
[1] https://www.polestar.com/de/ (Homepage, Access 26.03.2023)
[cs 26.03.2023, 17.12.2025]
REE Automotive [↑] [↓] [⇑] [⇓]
REE Automotive is a Platform start-up from Israel founded in 2019 by Daniel Barel and Ahishay Sardes, both of whom previously built the wheelchair company Softwheel. REE has developed electric corner modules (“REEcorner”) that integrate all drive components in a compact design, i.e. tires, e-motor, power electronics, wheel suspension and drive shafts.
The company is currently experiencing financial difficulties. In response, REE announced in 2025 that it would suspend the originally planned series production and focus on software development and technology licensing for OEM partners in the future.

Powertrain platform from REE Automotive
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy REE Automotive Ltd. [Homepage])

Demo vehicle with Morgan Olsen body
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of REE Automotive Ltd. [Homepage])
In fiscal year 2023, REE generated revenue of around €1.45 million, while in 2024, revenue of only around €0.56 million was reported. No reliable figures are available for 2025 yet, but the trend indicates that revenues will remain very low. At the same time, REE recorded high losses: for the past fiscal year, an operating loss of over $79 million and a net loss of around $112 million were reported, with a very low equity ratio. These figures show that the company is experiencing considerable financial difficulties.
There is little concrete information available on sales figures. In 2023, 25 test vehicles were manufactured, and production of the P7-C began at the end of the same year, but without any documented delivery figures. There are no confirmed sales figures for 2024 and 2025, including for possible exports to Europe. Although REE reported orders in the triple digits, it did not disclose how many vehicles were actually produced or delivered. Information on battery cells comes mainly from previous technical partnerships.
It is known that REE used battery packs from Microvast at times, but current information on cell manufacturers is not available.
REE Automotive is listed on the stock exchange, including in Frankfurt (ISIN IL0011786154, WKN A3CWAC).
Sources
[1] https://ree.auto/ (Homepage, Access 27.03.2023)
[cs 26.03.2023, 18.12.2025]
Rimac Automobili [↑] [↓] [⇑] [⇓]
Rimac is a Croatian BEV start-up based near Zagreb, founded in 2009 by Mate Rimac. The company develops and manufactures electric sports cars as well as components and drive systems for other car manufacturers. Porsche AG holds a 24% stake in Rimac [1]; both companies also own the hypercar company Bugatti Rimac, with Rimac being the majority shareholder with 55%.
With models such as the Nevera, Rimac focuses on an exclusive, high-performance segment at the upper end of the automotive market. Production of the Nevera, a fully electric hypercar with an extremely powerful drive system, is limited to a small number of units; originally, up to 150 vehicles were planned.
Reliable, publicly reported annual sales figures are not available due to the small number of units produced. Internal data indicates that only a portion of the maximum Nevera production had been delivered by the end of 2023, and official full-year data for Rimac vehicles alone is missing for 2024 and 2025; Combined figures for Bugatti Rimac Group deliveries are reported at just under 140 vehicles in total for 2025, indicating an increase over previous years.
Rimac also operates a components division, Rimac Technology, which develops powertrains, battery packs, and electrification systems for OEM partners. Collaboration with other automakers is boosting exports in Europe, North America, and Asia, although no separate regional export figures have been published for the limited-edition models.
On a financial level, Rimac is managed in the consolidated group under the umbrella of the Bugatti Rimac Group, which reported consolidated sales of approximately €310 million for 2024 and recorded a significant increase in sales to around €860 million for 2025, more than double the previous year’s figure, underscoring the positive business development.

Supercar Rimac Nivera – Exterieur
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of Rimac Automobili d.o.o. [Press Kit])

HV Battery from Rimac Nivera
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of Rimac Automobili d.o.o. [Press Kit])
The Nivera has four electric motors close to the wheels and a battery with a capacity of 120 kWh. The technical data is impressive, with an output of 1.4 MW (1914 hp), acceleration from 0-100 km/h in 1.97 seconds, and a top speed of 412 km/h.
Rimac uses 4680 format round cells. Lithium manganese nickel oxide (LMNO) is to be used as the cathode chemistry, which enables a higher cell voltage (5 V) and higher energy density compared to NMC [2].
The cell supplier for the Rimac Nivera is not known to the editorial team, but according to its website, Rimac works with round cells from various manufacturers.
In September 2023, a cooperation between Rimac and the Chinese cell manufacturer EVE Energy was announced at the IAA. According to a press release, EVE will build a cell factory for 46xx cells in Europe by 2027, and Rimac will produce battery packs and battery systems based on these cells [3].
There are no more recent reports on the cooperation between Rimac and EVE. However, it is known that EVE is setting up cell production in Hungary to supply BMW for the “New Class.”
At the IAA 2025 in Munich, Rimac Technology announced a strategic cooperation with Taiwanese battery manufacturer ProLogium: As part of a memorandum of understanding (MoU), both companies agreed to develop a solid-state battery platform, with ProLogium contributing its solid-state cells.
Sources
[1] https://www.rimac-automobili.com/ (Homepage, Access 27.03.2023)
[2] https://www.orovel.net/insights/the-rimac-nevera-battery (Access 27.03.2023)
[3] https://www.rimac-newsroom.com/press-releases/rimac-technology/rimac-technology-and-eve-energy-announce-collaboration-on-battery-cell-production (Access 14.09.2023)
[cs 27.03.2023, 14.09.2023, 28.12.2025]
Rising Auto was a New BEV brand from SAIC Motor, the largest state-owned car manufacturer in China. Due to sharply declining sales figures, SAIC decided to discontinue Rising Auto as a brand and continue it as a premium product line.
SAIC itself achieved sales of around RMB 653 billion (≈ €83.7 billion) in 2024. Net profit amounted to approximately RMB 1.66 billion (≈ €211 million), representing a decline of over 80% compared to the previous year. The company sold around 4.64 million vehicles, including approximately 1.37 million NEVs and around 1.08 million exports or overseas sales.
Rising Auto traces its roots back to British vehicle manufacturer Rover, the maker of iconic vehicles such as Range Rover and Land Rover. In 2004, SAIC acquired the rights to the 25 and 75 series from Rover, without taking over the trademark rights. Instead, SAIC created the new Roewe brand, which means “glorious power.” Under this brand, SAIC sells a wide range of vehicles, from combustion engines and hybrids to battery-electric vehicles.
The Rising Auto sub-brand was established in 2021 for Roewe’s BEV models, debuting with models such as the R7 SUV and the F7 sedan. However, Rising Auto’s sales volume remained very moderate; in 2023, around 14,230 vehicles were sold, and in 2024, only just under 2,090 units.
At the end of 2024, SAIC Motor therefore decided to discontinue the Rising Auto brand, with Rising Auto models continuing to be produced and marketed under the Roewe umbrella brand.

Rising Auto SUV R7
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of SAIC Motor Corporation Limited [Homepage])

Rising Auto sedan F7
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of SAIC Motor Corporation Limited [Homepage])
The batteries come from the SAIC/CATL joint venture United Auto Battery System (UABS). A larger NMC traction battery is planned for certain models, which is designed to be battery-replaceable. The underlying replacement technology was developed by SAIC Motor in collaboration with Aulton New Energy and is conceptually based on systems established in China, such as those used by NIO.
However, it is currently becoming apparent that CATL intends to press ahead with the further expansion of the battery replacement infrastructure on its own, while SAIC is focusing more on vehicle development. The originally communicated expansion targets of up to 10,000 replacement stations in China by the end of 2025 have not been achieved [1].
Sources
[2] https://carnewschina.com/2023/03/27/rising-auto-f7-from-saic-launched-in-china-with-swappable-batteries-starts-at-30500-usd (Access 31.05.2023)
[cs 31.05.2023, 08.06.2023, 25.12.2025]
Rivian Automotive [↑] [↓] [⇑] [⇓]
Rivan Automotive was founded in 2009 as a BEV start-up by Robert Scaringe in Irvine, California, albeit under a different name. Investments by Amazon and Ford brought Rivian to the attention of a wider audience, although Ford has since withdrawn its financial involvement [1].
In 2024, the announcement of a partnership with VW made headlines.
In 2029, Amazon commissioned Rivian to develop and produce battery-electric delivery vans. The framework agreement provided for the purchase of up to 100,000 vehicles by 2030. As of 2024, more than 20,000 Rivian delivery vans are in use in the US.
Originally, the Amazon order was subject to an exclusivity clause, but this was lifted in 2023 [2]. This enabled Rivian to develop additional vehicle models based on the Amazon delivery van [3]:
- The R1T is a typical US light truck with a length of around 5.5 meters. The model is available with three battery sizes of approximately 105, 135, and 180 kWh, with all four wheels powered by wheel-mounted electric motors. In the 2024 model year, Rivian also introduced an entry-level version with rear-wheel drive (RWD). In the premium BEV category, the R1T received the J.D. Power award for highest customer satisfaction in ownership in the US [4].
- The R1S is a large SUV with a length of around five meters, which is largely based on the powertrain of the R1T. Once production has stabilized, exporting this model to Europe is considered a possibility, but no concrete timelines or sales figures for the European market have been published yet.
The cooperation between Rivian and VW, which began in 2024, is organized as a joint venture:
- Rivian contributes its software-defined vehicle architecture, zone-based E/E architecture, and centralized vehicle software.
- VW is providing the financial investment, which is to gradually amount to around US$5 billion, and is contributing its global production expertise and access to the Group’s volume and premium brands.
The aim of the collaboration is to develop a uniform, scalable software and electronics platform. The jointly developed architecture will initially be introduced in future electric vehicles from the core Volkswagen brand, but will also be made available to other Group brands in the future.
No specific allocation to individual series models or model ranges has been communicated yet. For Rivian, the cooperation means not only technology transfer but also strategic and financial security, while Volkswagen aims to reduce its lag in software architectures and development times in the BEV sector.

Rivian R1T
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of Rivian Automotive, Inc. [Homepage])

Rivian R1S
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of Rivian Automotive, Inc. [Homepage])
Rivian’s sales initially showed growth after ramping up production. In 2023, the company delivered around 50,000 vehicles; in 2024, sales remained at a similar level with around 51,000 units. With these figures, Rivian lagged significantly behind Tesla, but also behind the two traditional OEMs GM and Ford, which each sold around 100,000 BEVs in 2024. However, Rivian sold significantly more BEVs than its US competitor Lucid.
For 2025, Rivian forecast lower production and sales volumes of around 41,000 to 43,000 vehicles due to subdued demand and a difficult market environment. Regular vehicle sales in Europe have not yet taken place.
In line with the still low sales figures, the company recorded high losses, a significantly negative cash flow, and a persistently high capital requirement. In 2024, the annual loss amounted to approximately $4.7 billion, and no operating profit is expected in 2025 either. Rivian responded with cost-cutting programs and personnel measures. However, financial stability is considered secure in the short to medium term thanks to existing liquidity reserves and close business relationships with VW and Amazon.
Rivian uses 2170 round cells from Samsung SDI, with the battery packs having a two-layer structure. In the maximum configuration, 9 packs are integrated into the battery [5].
Rivian Automotive is listed on the stock exchange, including in Frankfurt (ISIN US76954A1034, WKN A3C47B).
Sources
[1] https://electrek.co/guides/rivian/#h-the-history-of-rivian (Access 29.03.2023)
[2] https://www.electrive.net/2023/03/14/rivian-will-wohl-amazon-exklusivvertrag-abaendern (Access 29.03.2023)
[3] https://rivian.com/ (Homepage, Access 29.03.2023)
[4] https://rivian.com/newsroom/article/rivian-r1t-earns-highest-satisfaction-ranking-by-jd-power (Access 29.03.2023)
[5] https://insideevs.com/news/592649/munro-rivian-r1t-battery-pack/#:~:text=Rivian%20uses%202170%2Dtype%20cylindrical,in%209%20double%2Dstack%20modules. (Access 29.03.2023)
[cs 29.03.2023, 18.12.2025]
SERES is a new NEV brand from the Chinese Seres Group [1].
SERES was originally a brand of a joint venture between Dongfeng Motor and the Seres Group, which was founded in Silicon Valley in the USA in 2016. The name is a palindrome, meaning it can be read from both sides. This is intended to express perfect symmetry, which is of great importance in Chinese mythology. The letters S, E, and R stand for Silicon Valley, electricity, and range, respectively.
In 2018/2019, Dongfeng ended its cooperation with the former Sokon Group, which has since been renamed Seres Group. Dongfeng itself is one of the four major state-controlled vehicle manufacturers in China; Dongfeng ranks fourth alongside SAIC, Changan, and FAW.
In addition to the SERES brand, the Seres Group operates other BEV brands, in particular the AITO brand developed with Huawai, which is significantly more successful.
SERES positions itself as a NEV brand with a focus on electric SUVs and crossovers. Its portfolio includes the Seres 3 (compact BEV SUV), the Seres 5 (larger BEV SUV), and the Seres SF5, which was offered both as a pure BEV and with a range extender drive (EREV). SERES is also associated with larger SUV models such as the Seres 7, which primarily rely on EREV technology.
BEV models dominate SERES’ exports, while range extender models account for a higher share of the Chinese market. Depending on the market, BEVs account for roughly 40-60% and EREVs for 40-60%, with a clear shift in favor of EREVs for larger SUV models in China.
Sales of the SERES brand initially started successfully, but slumped significantly in 2024:
- In 2023, around 94,400 vehicles were still delivered.
- In 2024, only 40,000 units were delivered.
- In 2025, sales are estimated at 50,000 vehicles sold.
The Seres Group’s financial figures are not broken down by individual brands. However, given the low sales volumes, it can be assumed that the SERES brand is not profitable:
- In 2024, Seres Group generated revenue of around RMB 145.2B (≈ € 18.6B) and a net profit of just under RMB 6B (≈ € 760M).
- In the first half of 2025, revenue amounted to around RMB 62.4B (≈ € 8B), with net profit of around RMB 2.94B (≈ € 380M).

Seres 5 – Exterieur
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of CHONGQING SOKON MOTOR(GROUP)IMP.&EXP.CO.,LTD [Homepage])

Seres 5 – Interieur
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of CHONGQING SOKON MOTOR(GROUP)IMP.&EXP.CO.,LTD [Homepage])
Sales of the Seres brand in Europe remained low in 2023 and 2024, ranging in the low four-digit range across several countries, according to available market data. No reliable sales figures for Europe are available for 2025 yet. The focus of sales remains clearly on the Chinese domestic market.
There is much to suggest that the Seres Group will focus on the AITO brand in the future. AITO is now clearly the group’s strongest brand in terms of sales and margins, benefiting greatly from the Huawei partnership, utilizing its distribution network, and clearly dominating the group’s NEV sales. In 2024, AITO accounted for over 90% of NEV sales, while SERES played only a minor role in terms of volume.
For batteries, the Seres Group relies on cells from CATL.
Sources
[1] https://en.seres.cn/ (Zugriff 16.12.2025)
[cs 30.03.2023, 05.06.2023, 18.12.2025]
Slate Auto is a US BEV start-up founded in 2022 by Miles Arnone, William Barker, Jeff Wilke, and others. The company is headquartered in Troy, Michigan, while design and development are partly based in California. Series production is planned in a converted industrial facility in the US state of Indiana, with production currently scheduled to start at the end of 2026.
Slate’s business model differs from that of many other startups. The focus is on a radically simplified base vehicle that is delivered with as few permanently installed components as possible. The Slate Truck does without numerous comfort and infotainment features in its basic configuration, relying instead on robust, conventional technology and strong smartphone integration. Retrofittable components and kits allow the pickup to be gradually customized or converted, for example into a closed SUV with an additional row of seats. The aim is to keep production costs low while offering customers a high degree of flexibility.
Among the best-known investors is Amazon founder Jeff Bezos; the company has raised over half a billion US dollars. Compared to many other start-ups, its financing is considered solid, even though Slate has not yet delivered any production vehicles.
The powertrain is designed for cost efficiency and consists of
- only one 150 kW electric motor for rear-wheel drive and a single-speed transmission,
- two battery options with 52.7 kWh for a range of around 150 miles (~240 km) or 84.3 kWh for a range of 240 miles (~390 km), and
- charging systems for private and public charging with 11 kW and 120 kW, respectively.

Slate vehicle as a pickup or SUV variant
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of Slate [Press Release]
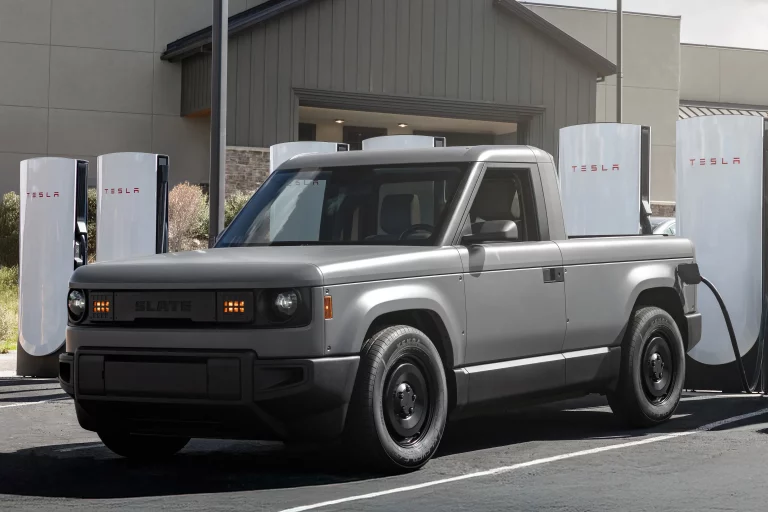

Fast charging at Tesla Supercharger
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of Slate [Press Release])
Originally, Slate’s marketing concept was closely linked to government subsidies for electric vehicles in the US. The starting price of the truck was to be below $20,000, taking into account the federal tax credit at the time.
With the elimination or reduction of these subsidies, the company itself estimates that the base price without subsidies will be around $25,000. This means that the Slate Truck will remain cheaper than other electric pickups, but it will lose some of its unique selling point, as conventionally powered pickups are already available in the entry-level segment at this price.
Against this backdrop, Slate’s market opportunities must be assessed in a differentiated manner. The comparatively high level of interest in the form of reservations indicates that there is fundamental demand for a simple, affordable electric vehicle.
The battery is supplied by SK On and uses lithium-ion cells with NCM chemistry; the cell format is likely to be large-format pouch cells, which are part of the manufacturer’s standard portfolio and enable comparatively high energy density with moderate installation space.
Sources
[1] https://www.slate.auto/ (Access 18.01.2026)
[cs 24.01.2026]
Sono Motors was founded in 2016 as a Solar-Car start-up in Germany; the business model envisaged was similar to Aptera and Lightyear.
Despite many years of development work, the Sion solar electric car project could not be brought to series production. Repeated delays, rising costs, and high financing requirements led to the discontinuation of vehicle development in 2023. The company ran into financial difficulties and initiated insolvency and restructuring proceedings. The withdrawal from automobile manufacturing represented a fundamental change in strategy.

Vehicles equipped with solar technology from Sono Motors
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of SONO MOTORS GmbH [Homepage])
Following restructuring, the company is now focusing exclusively on its solar technology business. This is being operated under the new name SonoSolar. The focus is on the development, integration, and marketing of solar systems for commercial vehicles, buses, trucks, and other mobility applications.
Financially, the company is still in a development and stabilization phase. The published financial data of the parent company shows that although initial commercial sales have been achieved and positive net results were reported in 2025, these are mainly based on balance sheet and non-cash effects. Operating revenues are still low. Sustainable profitability from the operating solar technology business has not yet been achieved at this stage.
Sources
[1] https://sono-solar.com/ (Access 23.12.2025)
[cs 04.04.2022, 23.12.2025]
Tesla is a Californian BEV start-up and the pioneer of electric mobility in the 21st century. The company was founded in California in 2003 by Martin Eberhard and Marc Tarpenning; a key catalyst is said to have been GM’s decision to recall the battery-electric vehicle EV1 against the will of the vehicle owners.
As part of one of the early financing rounds, Elon Musk also invested in the company in 2004 and gradually took control of Tesla, leading the two founders to leave in 2008 [1]. Within 20 years, Elon Musk developed the start-up into the world’s largest manufacturer of battery–electric vehicles with the help of innovative technologies and an intelligent model policy [2]. You can read a detailed report on Elon Musk’s strategy for success and his influence on the automotive industry in our Tesla Story.
Following Tesla’s meteoric rise, which triggered a profound transformation in the global automotive industry, Elon Musk is now planning a strategic realignment:
- Tesla is to be transformed from a traditional car manufacturer into an AI company.
- Production of the premium Model S and Model X will be discontinued in Q2 2026 to free up manufacturing capacity at the Fremont plant for new business areas.
- In the future, the focus will be more on future technologies such as humanoid robots (“Optimus”) and self–driving robotaxis (“Cybercab”).
The change in strategy comes against a backdrop of stagnating sales figures:
- In 2023 and 2024, around 1.8M vehicles were still delivered each year.
- In 2025, sales fell to just under 1.64M units, representing a decline of around 8.6%.
As a result, Tesla lost its title as the world’s largest BEV producer to BYD in 2025; the Chinese competitor sold 2.25M BEV models during the same period.
The reasons for the stagnation are complex. They range from increasing competition in the BEV segment and a lack of model diversity at Tesla to the polarizing public persona of Elon Musk. The declining sales figures are also affecting revenue and profits:
- Tesla’s revenue was around $ 97.7B in 2024 and fell to around $ 94.8B in 2025.
- Profits fell from around $ 7.1B in 2024 to around $ 3.8B in 2025, a decline of approximately 46%.
Tesla had previously enjoyed a meteoric rise in the automotive industry:
- The first Tesla model was launched in 2008 and was a small, sporty roadster based on the Lotus Elise. Only 2,450 of these vehicles were produced in a small series in England. Despite the small number of units, Tesla was able to gain important experience with electric drives.
- In 2012, the Model S, the first completely self-developed vehicle, was launched. The luxury sedan surprised with a range of 500 km, which was groundbreaking at the time.
- The Model X SUV, built on the same platform, followed in 2015.
- With the Model 3 sedan, Tesla became a volume manufacturer in 2017.
- The Model Y SUV was then developed on the basis of the Model 3, with production starting in 2020.
At the same time as the Model S went on sale in 2012, Tesla became the first vehicle manufacturer to set up its own charging network; as of 2025, Tesla customers worldwide had access to more than 75,000 fast-charging stations. Due to their high density and availability, Tesla Superchargers in the US are now also used by other OEMs, including GM, Ford, BMW, and Mercedes.

Tesla Model 3
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of Pixabay [tesla-5937063__340)

Tesla Model Y
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of Tesla, Inc. [Homepage])
The two premium products, Model S and Model X, are still produced exclusively at the production facility in Fremont, California, which was taken over from GM and Toyota.
Model 3 and Model Y are also manufactured at the main plant in Fremont, but the production capacity for the two high-volume series is far from sufficient. Tesla has therefore gradually opened new production facilities – known as Gigafactories – in Asia, North America, and Europe. Production of the Model 3 and Y began in Shanghai in November 2019, followed by the SOP of the Model Y in Austin, Texas, in March 2020 and in Brandenburg, Germany, in March 2022 [3, 4].
Tesla has been working on expanding its portfolio for some time, but has not been very successful so far.
With the Cybertruck, available since 2024, Tesla is targeting the pickup truck market segment, which is very important in the US and has traditionally been dominated by Ford with its F-Series for years. However, the polarizing design and high price of the Cybertruck do not appeal to the more conservative customers in this market segment:
- In the US, sales figures for the Cybertruck are falling well short of expectations. Kelley Blue Book estimates that just under 39,000 Cybertrucks will be sold in 2024 and around 16,000 units in the first nine months of 2025.
- In many markets outside the US, the Cybertruck cannot be sold or registered.
An entry into heavy–duty electric transport (Class 8) has also been planned for some time. After the Semi was unveiled in 2017, the start of series production was postponed several times, partly due to battery shortages, limited production capacity, and the prioritization of other vehicle programs. The first models have been in use by selected customers since the end of 2022, and the actual ramp-up of production is now planned for 2026.
The delays with the Semi have meant that Tesla has lost its unique selling point. With the Freightliner eCascadia, Daimler Truck, among others, already offers a battery-electric Class 8 tractor that is already in use by North American fleets.
Tesla initially used round cells with different formats and cell chemistry variants for the traction battery. The Model S and Model X feature 18650 cells, while the Model 3 and Model Y feature 2170 cells from Panasonic. The Chinese plant in Shanghai is supplied with cells from LG Energy Solution, which are also produced directly in China [5].
Since 2020, Tesla has also been sourcing prismatic cells from CATL for the base versions of the Model 3 and Model Y produced in Shanghai. These cells are mainly used in vehicles with standard range.
The Panasonic cells use NCA as their cell chemistry, LG mainly relies on classic NCM compounds as cathode material, while CATL’s prismatic cells are based on cobalt-free LFP chemistry. The latter is characterized by higher cycle stability and thermal stability, but has a lower energy density.
The switch to even larger round cells in the 4680 format has been planned for several years, but is proving complex. In particular, the industrialization of the new cell architecture (“tabless design”) and the scaling of the dry coating of the electrodes have led to lower yields and production bottlenecks. As a result, 4680 cells have not yet been manufactured in the quantities and quality originally planned.
The 4680 cell is a central element of Tesla’s long-term battery cell and vehicle strategy. Its larger dimensions, lower number of individual cells, and integration into a structural battery pack are intended to reduce costs and stiffen the vehicle structure. In practice, the dry coating of the cathodes proved to be particularly challenging from a technical standpoint, as it is sensitive to process fluctuations and the achievable energy density initially fell short of expectations.
These problems primarily affected models that were explicitly designed for use with 4680 cells. The Model Y produced in Texas with a structural battery pack was temporarily delivered exclusively with 4680 cells, but in limited quantities. The Cybertruck also relies on 4680 cells, although Tesla is initially opting for conservative performance parameters in order to reduce cell stress and increase production stability.
The Tesla Semi is also planned to use 4680 cells. However, due to the high energy requirements and the necessary cycle stability, a specially optimized version of the cell will be used here. The slow scaling up of 4680 production is considered one of the reasons for the Semi’s limited production rate to date.
Tesla is listed on the stock exchange, including in Frankfurt (ISIN US88160R1014, WKN A1CX3T).
Sources
[1] https://www.nau.ch/news/wirtschaft/tesla-die-geschichte-des-elektroauto-giganten-65921960 (Access 11.04.2023)
[2] https://www.enbw.com/blog/elektromobilitaet/trends/verkaufszahlen-e-autos-das-sind-die-meistverkauften-stromer-2022 (Access 11.04.2023)
[3] https://teslawissen.ch/wo-baut-tesla-seine-fahrzeuge-tesla-werke-weltweit/#:~:text=Fremont%2C%20USA%20%E2%80%93%20Kalifornien&text=Es%20ist%20aktuell%20die%20einzige,auch%20das%20Model%20Y%20dazu.
[4] https://cleantechnica.com/2023/04/05/tesla-plans-to-manufacture-4-million-less-expensive-electric-cars-each-year (Access 11.04.2023)
[5] https://insideevs.com/news/587455/batteries-tesla-using-electric-cars (Access 14.04.2023)
[cs 14.04.2023, 03.01.2026, 01.02.2026]
Togg Auto is a New-Country start-up founded in 2018 on the initiative of President Erdoğan, among others, by the Anadolu Group, BMC, the Kök Group, Turkcell, and Zorlu. The name stands for Türkiye’nin Otomobili Girişim Grubu in Turkish, which translates as “Turkish Automobile Joint Venture Group” [1].
Togg’s first production model is a mid-size battery-electric SUV called the T10X, with exterior design by Pininfarina. The vehicle is available with two different battery sizes. The smaller version has a usable capacity of 52.4 kWh and achieves a range of around 314 kilometers according to WLTP, while the larger 88.5 kWh battery enables a range of up to 523 kilometers. The maximum charging power is up to 150 kW at DC fast charging stations and up to 22 kW for AC charging [2].
Official reservations for the T10X began on March 16, 2023, via the company’s own online platform. Within just twelve days, Togg registered over 175,000 pre-orders [3], but actual sales figures were slightly lower:
- In its first full year of sales in 2023, Togg sold around 19,500 vehicles, almost exclusively in the Turkish market.
- In 2024, the manufacturer significantly increased its sales and achieved a leading position among battery electric vehicles in Turkey with around 30,000 units sold.
- Preliminary market data for 2025 shows high registration figures again until autumn, which are already significantly above the previous year’s level, so that sales of around 40,000 vehicles are expected for the year as a whole, with the focus remaining clearly on the domestic market.
Economically, Togg is still in a start-up phase. Continued losses are expected for the 2024 and 2025 fiscal years, as is typical for capital-intensive electric vehicle start-ups. Industry analyses assume that Togg will only be able to break even once production and sales volumes are significantly higher. There are no indications of acute liquidity problems to date, but the company continues to be supported by its shareholders and government subsidies.

Togg Model T10X – Exterieur
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of Türkiye’nin Otomobili Girişim Grubu Sanayi ve Ticaret A.Ş [Homepage])

Togg Model T10X – Interieur
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of Türkiye’nin Otomobili Girişim Grubu Sanayi ve Ticaret A.Ş [Homepage])
Structured exports to Europe did not begin until 2025. Market entry in Germany took place towards the end of 2025 with an initially very limited number of units, so that only low three-digit sales figures are expected in Europe for 2025. Germany is considered a kind of secondary home market for Togg, as a large population group with Turkish roots lives there and has a high level of awareness and emotional affinity for the brand.
For cell and battery production, Togg founded the joint venture Siro together with the Chinese battery manufacturer Farasis Energy [4]. The battery cells are manufactured in NMC chemistry in pouch format and assembled into battery packs in the immediate vicinity of the vehicle plant in Gemlik. This vertical integration is intended to secure long-term cost advantages and strengthen the manufacturer’s technological independence.
Sources
[1] https://www.togg.com.tr/ (Homepage, Access 05.04.2023)
[2] https://www.auto-motor-und-sport.de/elektroauto/tuerkei-elektroauto-togg-suv-t10x-limousine (Access 05.04.2023)
[3] https://insideevs.de/news/659860/togg-t10x-175000-vorbestellungen-elektroauto (Access 05.04.2023)
[4] http://siro.energy/ (Access 05.04.2023)
[cs 05.04.2023, 23.12.2025]
Vinfast is a Vietnamese New-Country start-up for passenger cars and electric motorcycles, founded 2017 by Mr. Pham Nhat Vuong in Hai Phong [1]. He was previously very successful in Ukraine in the food industry and then built the conglomerate Vingroup in Vietnam; business areas include education, health and tourism.
Vinfast’s corporate history is closely linked to German suppliers, thanks mainly to former BMW manager Quang-Hue Vo and his good contacts in the German automotive industry [2]. Vinfast initially began producing internal combustion vehicles with BMW technology; the company now develops its own battery-electric SUV models, canonically named VF6, VF7, VF8, and VF9, covering different market segments.
In 2023, VinFast began systematic international sales of its BEV models. Global deliveries in 2023 were still at a comparatively low level and were mainly achieved in the domestic market of Vietnam. In 2024, the company recorded a significant increase in sales and delivered around 97,000 battery electric vehicles worldwide, with Vietnam continuing to account for the majority of sales. For 2025, VinFast has already reported more than 110,000 units delivered in the first nine months, indicating continued volume growth.
Financially, VinFast remains in a loss-making start-up phase. For the 2024 financial year, the company reported revenue equivalent to around $1.8 billion, but at the same time a net loss of over $3 billion. In 2025, rising revenues but continued high losses were also reported. Expansion, high investments in production, sales, and infrastructure, as well as market entry in several regions, are weighing significantly on earnings.

Vinfast model VF8
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of VinFast Germany GmbH [Homepage])

Vinfast model VF9
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of VinFast Germany GmbH [Homepage])
Exports to Europe began in 2023, but remained very limited in terms of volume in 2023 and 2024. Even in 2025, sales figures in Europe, including Germany, remained in the low three–digit range. VinFast adjusted its European strategy and largely discontinued direct sales in order to sell through dealer networks in the future.
VinFast’s battery and cell strategy is based on a combination of in-house expertise and international partnerships:
- In 2021, Vingroup founded the battery subsidiary VinES, which is setting up LFP cell production in Vietnam in collaboration with Chinese cell manufacturer Gotion. The joint venture includes an LFP battery cell factory with a planned annual capacity of around 5 GWh in Hà Tĩnh province (Vietnam). However, there is currently no officially confirmed information on the ramp-up or the actual production volume achieved [3].
- In addition, there are technology and supply relationships with CATL, including in the field of modern battery architectures.
- VinFast is also cooperating with Taiwanese cell manufacturer ProLogium on the development of solid-state batteries [4].
Sources
[1] https://vinfastauto.eu (Homepage, Access 07.04.2023)
[2] https://www.handelsblatt.com/unternehmen/industrie/marke-vinfast-startet-wie-die-deutsche-wirtschaft-vietnam-ein-auto-baut/23125950.html (Access 07.04.2023)
[4] https://vines.net.vn (Access 07.04.2023)
[4] https://www.bestmag.co.uk/vinfast-and-prologium-to-commercialise-solid-state-battery-technology-for-evs (Access 07.04.2023)
[cs 05.04.2023, 22.12.2025]
Voyah is a new BEV brand from Chinese carmaker Dongfeng, which was only founded in 2021 [1].
Dongfeng Motor itself sold around 2.5 million vehicles in 2024, generating revenue of approximately RMB 106 billion (≈ €14 billion). This puts Dongfeng in fourth place among the four major Chinese state-owned OEMs.
The first Yoyah model is an SUV called the Voyah Free, which, at 4.9 m long, is comparable to the Mercedes-Benz EQE SUV. In China, the vehicle is also offered as a range extender. This variant has a 33 kWh battery, which enables a pure electric range of around 140 km according to NEDC. The BEV version is equipped with an 88 kWh traction battery and has a NEDC range of up to just under 600 km.
Since its market launch in China, sales figures have risen steadily:
- In 2023, almost 50,300 vehicles had already been delivered.
- In 2024, sales rose to over 80,100 units.
- In 2025, there was an even stronger increase to almost 150,170 units.
Dongfeng does not break down its sales figures by drive type, but according to unofficial sources, the share of BEVs in sales is very low.
Despite rising unit sales, Voyah is still considered to be operating at a loss; specific, separately reported profit figures for Voyah have not yet been published for 2024 and 2025. Only consolidated figures within the Dongfeng Group are available, which continue to show a high investment requirement in the NEV business.

Voyah Free – Exterieur
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of NOYO Mobility AG [Homepage])

Voyah Free – Interieur
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of NOYO Mobility AG [Homepage])
The Voyah Free was unveiled at the IAA 2023 in Germany [2]. At the same time, the model received EU type approval, enabling exports to all 27 EU member states as well as Norway, Switzerland, and Israel, among others [3]. Market entry in Europe began in early 2023 with an initial delivery of 136 vehicles to Norway [4]. Other markets such as Denmark, the Netherlands, Sweden, and Israel were then gradually addressed [5].
European sales figures have remained low so far, hovering in the low three-digit range in both 2023 and 2024; and no significant sales figures are expected for 2025 either, meaning that Europe is currently of strategic importance to Voyah, but not as a volume market.
It can be assumed that Farasis Energy lithium-ion pouch cells are used in the Voyah, as these are also used in other models from the Dongfeng Group.
Sources
[1] http://www.dongfeng-global.com/ (Access 10.04.2023)
[2] https://www.golem.de/news/bilanz-der-iaa-2023-alles-china-oder-was-2309-177492.html (Access 15.09.2023)
[3] https://www.chinapev.com/ev-2/voyah/dongfengs-ev-brand-voyah-free-has-obtained-eu-vehicle-certification (Access 10.04.2023)
[4] https://www.electrive.net/2023/01/03/voyah-liefert-erste-elektroautos-in-norwegen-aus (Access 10.04.2023)
[5] https://www.voyah.ch/ (Zugriff 15.09.2023)
[cs 10.04.2023, 02.08.2023, 15.09.2023, 22.12.2025]
Xiaomi has only been active in the automotive market since 2024 with its new new BEV brand, which was announced back in 2021 [1].
Xiaomi itself was founded in 2010 and is one of the world’s largest manufacturers of smartphones and connected consumer electronics; Xiaomi has ranked third in the global smartphone market for several years, behind Samsung and Apple.
Apple also pursued its own BEV projects for many years and carried out extensive development work, but completely discontinued these activities in 2024 without bringing a production vehicle to market. Xiaomi instead founded the subsidiary Xiaomi Automobile Co. Ltd. in 2021 and established its own vehicle production facility in Beijing. It entered the market in 2024 with the SU7 sedan.
Xiaomi is applying a strategy to automotive manufacturing that has already proven successful in the smartphone business: the targeted adoption of successful product concepts and their consistent further development:
- The SU7 is clearly based on the Porsche Taycan in terms of design, proportions, and overall appearance.
- The second model, the SUV YU7, is completely based on the Tesla Model Y.
In Western markets, this approach is often seen as copying, but in Chinese industry it is considered an established and rational business strategy: successful products are systematically analyzed, adapted, and improved in terms of functionality and cost structure.
A clear example of this improvement is the integration of broadband HUD (head-up displays):
- The concept was presented by BMW back in 2023, but will not be installed in the “New Class” vehicles until 2026.
- Xiaomi picked up on the concept and implemented it in both models just one year after BMW’s presentation.
- In the YU7 in particular, this significantly improves the user interface compared to the Tesla Model Y model.
The sales figures underscore the success of this strategy:
- In 2024, around 135,000 vehicles were delivered.
- In 2025, more than 410,000 units have already been sold.

Xiaomi SU7 – Exterieur
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of Xiaomi [Homepage])

Xiaomi YU7 – Interieur
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of of Xiaomi [Homepage])
Financially, the BEV business involved high investments in the initial phase, but reached the operating break–even point as early as 2025. Xiaomi only publishes limited separate business figures for the automotive division, but reports rising sales and an improved cost structure for 2024 and 2025.
Exports to Europe have been announced, but concrete sales figures for Europe are not yet available for the years 2023 to 2025. Market entry in selected European countries is expected in the second half of the decade at the earliest.
Xiaomi currently relies entirely on CATL for battery technology. For more powerful versions of the SU7 and for larger battery packs, Xiaomi uses NMC cells in modern high-energy-density formats, while LFP cells are also used in higher-volume versions.
Xiaomi is listed on the stock exchange, among others in Frankfurt (ISIN KYG9830T1067, WKN A2JNY1).
Sources
[1] https://www.auto-motor-und-sport.de/neuheiten/xiaomi-will-elektroautos-bauen/ (Access 22.05.2023)
[cs 22.05.2023, 19.12.2025]
Xpeng is a Chinese BEV start-up founded in 2014 by He Xiaopeng [1]. The company’s name is also derived from the founder’s last name. Previously, Mr. Xiaopeng had very successfully built up the Chinese Internet service provider UCWeb, this company he sold to Alibaba in 2014 for $4.3 billion.
In 2014, Mr. Xiaopeng was one of the first Chinese to receive a Tesla Model S. The vehicle is said to have impressed him so much that he decided to enter the automotive industry himself. Through his good industrial contacts, he managed to attract Alibaba as well as other Chinese companies such as Foxxcon as investors [2].
In 2023, Xpeng and VW agreed on a strategic cooperation.
The first model, the G3 SUV, was unveiled at CES Las Vegas in 2018, followed by the P7 sedan in 2019 and the slightly smaller P5 sedan in 2021. BEV sales figures have risen steadily since then:
- In 2022, only around 120,750 units were delivered.
- In 2023, there was a slight increase to around 141,600 vehicles.
- In 2024, just under 190,100 units were delivered.
- In 2025, sales more than doubled, rising to 430,000 cars.
Like many other BEV start-ups, Xpeng is not yet profitable, but is on its way to becoming so. The company was able to significantly reduce its net loss from 2023 to 2025 and could turn a profit for the first time in 2026:
- In 2023, XPeng generated revenue of RMB 30.7B (≈ € 4.3B) with a net loss of RMB 10.4B (≈ € 1.45B).
- In 2024, revenue rose to RMB 40.9B (≈ € 5.6B), while the net loss almost halved to RMB 5.8B (≈ € 0.8B).
- For 2025, the quarterly figures to date show a further increase in revenue to an expected annual level of over RMB 60B (€ 8B) with another significant reduction in losses. In the third quarter, the net loss was around RMB 0.38B (approx. € 0.05B).

XPeng P9 – Exterieur
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of XPeng Inc. [Homepage])

XPeng G9 – Interieur
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of XPeng Inc. [Homepage])
In July 2023, VW announced a strategic partnership with Xpeng, including a financial stake of just under 5%. Based on the G9 (SUV), two BEV vehicles in the Chinese B segment (wheelbase approx. 2.7–2.9 m) are to be produced under the VW brand from around 2026. This involves the use of Xpeng’s powertrain, assistance systems, electronics platform, and software.
The cooperation has since been steadily deepened: In July 2024, an agreement was reached on a joint E/E electrical/electronic architecture (“China Electronic Architecture” or CEA), which will apply not only to pure BEVs, but also to vehicles with internal combustion engines (ICE) and plug-in hybrids (PHEV) at VW in China. In addition, VW will license Xpeng’s XNGP (“intelligent driving”) assistance software for its first Chinese EVs starting in 2026. This makes Xpeng a technology partner of VW in China, particularly in the areas of software, E/E architecture, and rapid vehicle development.
Previously focused on battery electric vehicles, Xpeng announced a powertrain with range extender technology in November 2024, which is expected to enable a combined range of up to 1,400 km and a battery range of up to approximately 430 km. The new powertrain will be offered in the X9 and G7 models, among others.
Xpeng exported around 45,000 vehicles in 2025, with an estimated 10,000 units going to Europe. Since the third quarter of 2025, XPeng has been having its G6 and G9 models assembled at Magna Steyr in Graz using the SKD process, making it the first Chinese manufacturer to have such European production. This enables XPeng to circumvent the high EU tariffs and shorten delivery times for the European market.
Xpeng sources its battery cells from several major manufacturers and relies on a broad-based supply strategy. Its key partners include CABL, EVE Energy, SVolt, and BYD. While CALB and EVE Energy are playing an increasingly important role in various model series, BYD continues to supply its blade batteries, particularly for certain long-range versions. By spreading its supply across several suppliers, Xpeng reduces dependencies, increases security of supply, and can use different battery technologies depending on the vehicle segment.
Xpeng is listed on the stock exchange, among others in Frankfurt (ISIN HK0000264595, WKN A14Y51).
Sources
[1] https://www.xpeng.com/] (Access 24.11.2025)
[2] https://www.bolidenforum.de/artikel/allgemein/2575558-die-geschichte-des-elektroautoherstellers-xpeng (Access 14.04.2023)
[cs 14.04.2023, 15.09.2023, 24.11.2025, 08.02.2026]
Zeekr is a new BEV brand from the Zhejiang Geely Holding Group, which was founded in March 2021 [1]. In response to Tesla und NIO, Zeekr is set to focus on premium electric vehicles within the multi-brand group [2].
The Geely Holding Group (GHG) itself is one of China’s leading automotive OEMs, ranking third in terms of total sales behind BYD and SAIC. In 2025, GHG achieved total vehicle sales of around 4.12 million units, including all brands (Geely Automobile, Volvo Cars, Polestar, Smart, etc.).
No complete consolidated financial statements are published for GHG, only for Geely Automobile Holdings, which is included therein. Automobile Holding’s revenue in 2024 was RMB 240.2B (~€ 31B), with net profit of RMB 16.6B (~ € 2.1B); no consolidated financial figures are available for 2025 yet.
The brand Zeekr was founded in 2021 by Geely Holding Group and initially organized as an independent company called Zeekr Intelligent Technology. Following an IPO in 2024, the company was completely taken over by Geely Automobile Holdings in 2025 and integrated into the listed automotive division.
Zeekr launched as a pure BEV brand, with models including the Zeekr 001 (shooting brake/crossover), the Zeekr X (compact SUV), the Zeekr 7X (mid-size SUV), the Zeekr 007 (mid-size sedan), and the Zeekr 009 (large MPV). Technologically, the Zeekr models are based on the Geely Group’s Sustainable Experience Architecture (SEA).
With the Zeekr 9X, the brand is expanding its portfolio with a model featuring range-extender drive (REEV); however, sales remain clearly dominated by BEVs.
Sales figures have been rising since 2022, but have recently stagnated:
- In 2022, just under 72,000 units were delivered.
- In 2023, there was an increase to around 118,700 vehicles.
- In 2024, sales doubled and rose to around 222,100 units.
- In 2025, sales stagnated at just over 224,100 vehicles.
ZEEKR is not yet profitable, but has significantly reduced its losses:
- In 2023, revenue was around RMB 51.7B (≈ € 6.6B) and the net loss was around RMB 8.26B (≈ € 1.06B).
- In 2024, revenue rose to just under RMB 76B (≈ € 9.7B), while losses were reduced to just under RMB 1B (≈ € 130M).

Zeekr 001
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of ZEEKR EU B.V. [Press])

Zeekr X
(Mit freundlicher Genehmigung/Courtesy of ZEEKR EU B.V. [Press])
Zeekr began exporting to Europe in 2023. In Europe, the first vehicles were delivered in the low four-digit range in 2023. In 2024, European sales were around 6,000 to 7,000 units, with a focus on Sweden, the Netherlands, and Germany. A further increase to around 10,000 to 15,000 vehicles is expected for 2025, with Europe remaining a region of development and expansion.
ZEEKR sources its battery cells from CATL and uses, among other things, the Qilin battery, which is based on CATL’s Cell-to-Pack (CTP) technology. According to ZEEKR, the brand was one of the first vehicle manufacturers to introduce this technology in series-production vehicles, including the ZEEKR 001 and ZEEKR 009. The CTP architecture enables higher energy density at the pack level, thereby contributing to increased range.
ZEEKR went public on the New York Stock Exchange in May 2024 under the ticker symbol ZK, raising approximately $440 million in its IPO.
However, its parent company Geely is seeking a complete takeover and delisting, so ZEEKR is expected to return to being a privately held subsidiary.
Sources
[1] https://www.zeekr.eu/de-de (Access 15.09.2023)
[2] https://www.elektroauto-news.net/elektroautos/betrachtung-tesla-byd-nio-xpeng-zeekr-im-jahr-2022#:~:text=Der%20Blick%20auf%20Geelys%20Premium,6.007%20Auslieferungen%20im%20Jahr%202021. (Access 15.04.2023)[3] https://www.auto-motor-und-sport.de/elektroauto/geely-premium-e-autos-zeekr-001 (Access 15.04.2023)
[cs 16.04.2023, 15.09.2023, 18.12.2025, 08.02.2026]
